- GreenMatch
- Renewable Energy Transition: A UK vs US Analysis
Renewable Energy Transition: UK vs US Analysis

The global quest to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions has led to a significant shift towards renewable energy transition. The United States and the United Kingdom have emerged as critical players in this global shift.
The transformative shift in its energy landscape was driven by the urgent need to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement. This transition is primarily marked by a move from fossil fuels towards cleaner, renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass.
The transition to clean energy is happening worldwide and is unstoppable. It's not a question of 'if', it's just a matter of 'how soon' – and the sooner, the better for all of us.

The current state of renewable energy transition
In 2022, renewable energy sources accounted for about 13.1% of total US primary energy consumption and about 21.5% of utility-scale electricity generation. The nation's energy primarily comes from fossil fuels (79%), with nuclear energy contributing 8.0% and renewable sources making up 13.1%.
As of 2023, wind and solar are forecasted to account for 16% of total electricity generation, up from 14% in 2022. Significant investments in new solar and wind-generating capacity primarily drive this increase. The US electric power sector operated about 73 gigawatts (GW) of solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity at the end of 2022, with plans to expand solar capacity by 43% (32 GW) in 2023.
In the first half of 2023, renewables generated 25% of US power, with solar contributing 5.77% of total US electrical generation. This growth in renewable energy generation has been facilitated by the rapid expansion of energy resources, especially solar and wind, and the declining construction costs and favourable tax credits for solar capacity.
On the other side of the Atlantic, the UK has made significant strides in its renewable energy journey. In 2020, renewables accounted for more than 43.1% of the UK's total electricity generated. By 2022, this figure had risen to 40%. The primary renewable energy sources in the UK are wind power, plant biomass, and solar power.
As of the second quarter of 2023, renewable energy contributed 42.1% of total electricity generation. This growth has been driven by a 6% increase in renewable electricity generation capacity compared to the same quarter of the previous year, with offshore wind and solar growing by 9% and 8%, respectively.
However, despite these advancements, the UK's renewable energy capacity growth has been slower than the global average. In the past three years, the UK's renewable capacity has grown by an average of 4.45% per year, compared to a worldwide average of 9.67%.
A comparative analysis between the UK vs US
There is a stark contrast between the US and the UK regarding renewable energy usage. While the US still heavily relies on fossil fuels, the UK has made substantial progress in shifting towards renewable energy sources. In 2020, the UK marked a historic milestone when electricity generated from renewable energy sources outstripped that from fossil fuels.
The target set by the UK government is to decarbonise all sectors of its economy to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. As part of this strategy, the UK government has laid out policies and proposals to reduce emissions in each sector, with a significant focus on increasing the share of renewable energy
However, the UK's growth rate in renewable capacity has been slower than the global average. Additionally, the UK has attracted around £120 billion in investment in renewables since 2010 and is expected to attract a further £100 billion in net zero by 2030.
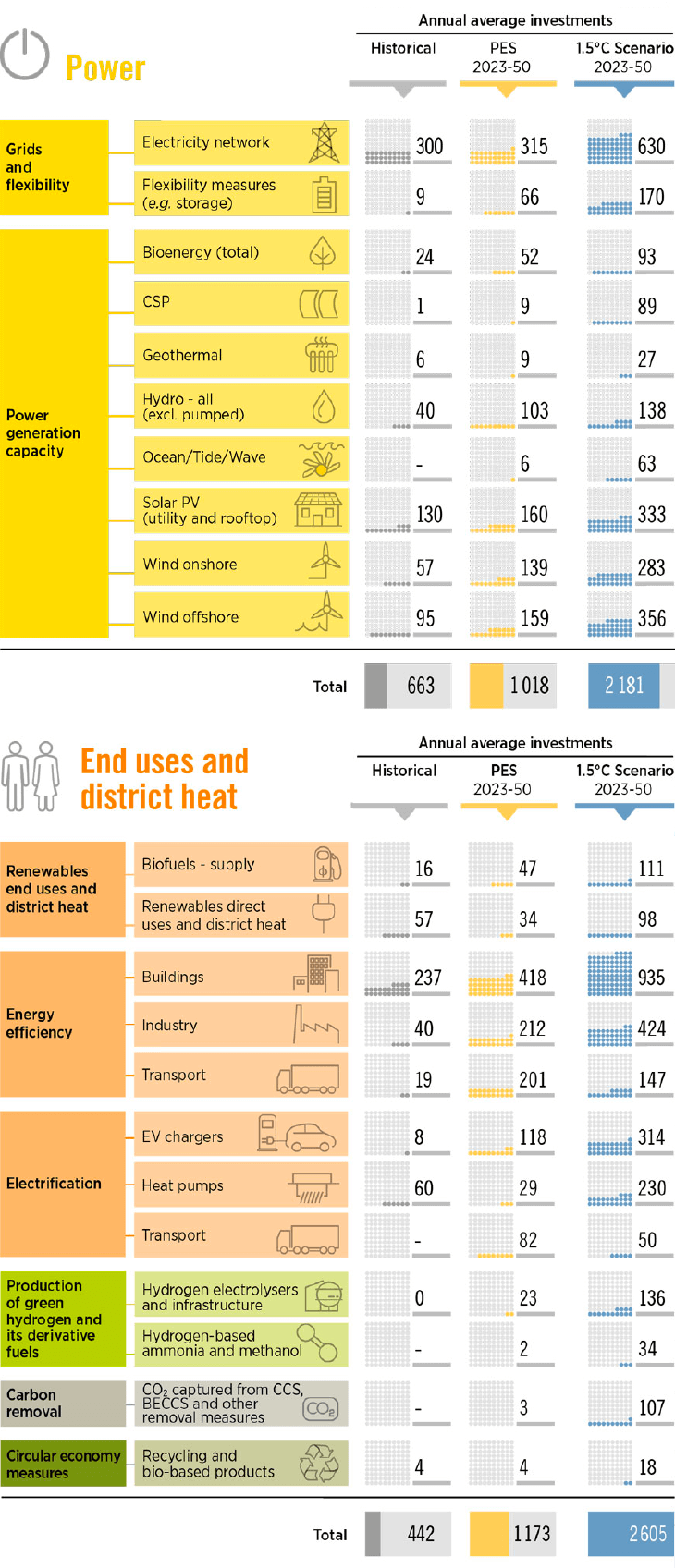
Key data points for renewable energy in the United States and the United Kingdom.
Table 1: Renewable energy in the United States
| Category | Data |
|---|---|
| Percentage of total primary energy consumption from renewables | 13.1% |
| Percentage of entire utility-scale electricity generation from renewables | 21.5% |
| Main renewable energy sources | Wind, hydropower, solar, biomass |
| Renewable portfolio standards | 36 states, the District of Columbia, and 4 US territories |
Table 2: Renewable energy in the United Kingdom
| Category | Data |
|---|---|
| Percentage of total electricity generated from renewables (2020) | 43.1% |
| Percentage of total electricity generated from renewables (2022) | 40% |
| Main renewable energy sources | Wind power, plant biomass, solar power |
| Carbon emissions reduction targets | 68% by 2030, 77% by 2035 (compared to 1990 levels) |
| Net-zero emissions target | 2050 |
| Heat pump grants | £7,500 for air source heat pumps, £7,500 for ground source heat pumps |
The primary sources of renewable energy
The United States and the United Kingdom have made significant strides in harnessing renewable energy, with the UK currently deriving a higher percentage of its energy from renewable sources than the US.
The US is projected to continue increasing its renewable energy consumption through 2050, while the UK is on track to increase renewable generation, with plans to expand offshore wind's output from 11GW to 50GW by 2030, and solar capacity could grow five-fold from 14GW to roughly 70GW in the same period.
| Country | Percentage of Total Electricity Generation from Renewables | Leading Sources of Renewable Energy |
|---|---|---|
| US | 20% | Wind, Solar, Biomass, Hydropower, Geothermal |
| UK | 47% | Wind, Solar, Bioenergy, Hydroelectric |
In 2020, renewable energy sources comprised a significant proportion of the electricity mix that powers homes and businesses. It was the first year in the UK's history that electricity came predominantly from renewable energy, with 43% of power coming from a mix of wind, solar, bioenergy, and hydroelectric sources. As of December 2020, renewable sources generated 41.4% of the electricity produced in the UK, which was around 6% of total UK energy usage.
In 2022, wind power contributed 26.8% of the UK's electricity generation. Biomass energy contributed 5.2% to the renewable mix. Solar power contributed 4.4%, and hydropower, including tidal, contributed 1.8%.
Progress towards renewable energy targets
Renewable energy sources have been gaining traction, with solar and wind energy leading the charge. According to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), wind and solar accounted for 14% of US electricity generation in 2022, and this figure is expected to rise to 16% in 2023 and 18% in 2024.
Investments in new solar and wind-generating capacity primarily drive the increase in renewable energy generation. The power sector operated about 73 gigawatts (GW) of solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity at the end of 2022, with plans to expand solar capacity by 43% (32 GW) in 2023.
This has been a remarkable achievement since 2022, when wind and solar power accounted for 14% of US electricity generation while the UK accounted for 20%. The share of renewable energy in the global energy mix increased from 16% in 2020 to 77% by 2050 in IRENA's 1.5°C scenario.
The United States and the United Kingdom have set ambitious targets for renewable energy. The UK has committed to reducing emissions to 68% by 2030 and achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. However, current policies are estimated to lead to 2030 emissions of 58–63% below 1990 levels, indicating that further action is needed.
Renewable energy production and consumption in the US reached record highs in 2022. This was driven mainly by record-high solar and wind energy production and increasing hydroelectric power production.
The share of renewable energy in the global energy mix is expected to increase from 16% in 2020 to 77% by 2050. The UK is on track to contribute significantly to this increase. The country's solar capacity was over 14.4 gigawatts (GW). The UK's alone renewable generation share rose 3.5 percentage points to 42.1%, and low-carbon generation rose 2.7 percentage points to 57.8%.
Investment and funding in renewable energy
The transition to renewable energy is a global imperative. The US and UK have made significant strides in attracting private and public investment in renewable energy, contributing to the worldwide shift towards cleaner energy sources.
Investment in renewable energy in the US has been robust, with an estimated $55.5 billion invested in 2021. This investment is driven by private-sector activity and public funding, with significant support from the federal government.
The UK has also seen substantial investment in renewable energy, with £12 billion invested in 2021. Various funding options, including government grants, loans, and private-sector investment, support this investment.
Private and public investment in renewable energy projects
In the United States, the renewable energy sector has seen a significant influx of private investment. In the past year, private investments in domestic clean energy projects and manufacturing facilities have totalled $271 billion, exceeding the combined clean energy investments made over the previous eight years.
This surge in investment has been driven by unprecedented federal support and incentives, leading to the announcement of 184,850 megawatts of new utility-scale clean energy capacity and the creation of 29,780 new manufacturing jobs.
However, challenges such as supply chain issues, inflation, and opposition driven by misinformation hinder renewable energy development and must be addressed to realise the incentives provided fully.
The private finance market for renewable energy is well established in the United Kingdom, with considerable personal investment in renewable energy projects across several sectors. The government's working group concluded that there are no general market failures in the supply of private finance for the renewable energy sector in Wales.
If projects provide sufficient commercially acceptable returns, capital investment is generally available from private markets. However, the group also identified that public finances must target specific gaps and market failures, such as community enterprises' issues accessing finance for projects adopting a shared revenue model.
Financing models and funding options
The federal government has significantly mobilised private sector investment in renewable energy in the US. Public investments are effective in advancing renewable energy goals and industrial policy priorities. For example, government R&D expenditures, feed-in tariffs, and taxes have been found to have positive effects on private investment.
By supporting nascent yet promising technologies when private financing institutions do not, the government is carving a path for clean energy projects.
In the UK, various finance options and funding support are available to help make renewable energy projects a reality. These include government schemes, local council support, and specialised products such as the Green Loan for energy efficiency in the public sector. The UK government also funds homeowners and businesses who export surplus energy from their systems to the grid.
However, challenges remain to be addressed, including regulatory hurdles, public acceptance, and supply chain constraints. By addressing these challenges and leveraging the available financing models and funding options, both countries can continue to drive the transition to renewable energy.
Challenges and opportunities
The US and UK face challenges in transitioning to renewable energy, including the need for significant infrastructure investment, regulatory hurdles, and public acceptance. Ensuring accurate measurements of global horizontal irradiance in solar and renewable energy efforts can also be challenging.
However, there are also unique opportunities for collaboration and knowledge sharing between the two countries, particularly in technology development, policy formulation, and financing mechanisms.
In terms of challenges for both the United States and the United Kingdom face several challenges in their transition to renewable energy, including:
- Infrastructure investment: Significant investments are required to upgrade and expand the existing energy infrastructure to accommodate the integration of renewable energy sources.
- Regulatory hurdles: Complex regulations and policies can slow the adoption of renewable energy technologies and hinder the development of new projects.
- Public acceptance: It can be challenging to gain public support for renewable energy projects, mainly onshore wind farms and large-scale solar installations.
- Supply chain constraints: The rapid growth of renewable energy demand can exacerbate supply chain constraints and interconnection bottlenecks, leading to increased costs and project delays.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, there are several opportunities for further expansion and innovation in the renewable energy sector in both the US and UK:
- Technological advancements: Continued innovation in renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems, can help reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Policy support: Supportive policies and incentives, such as renewable portfolio standards in the US and the UK's net-zero target, can help drive the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing: The US and UK can collaborate and share knowledge in technology development, policy formulation, and financing mechanisms to accelerate the transition to renewable energy.
- Investment in clean energy innovation: Both countries can invest in research and development to create new renewable energy technologies and solutions, fostering economic growth and job creation.
Future of renewable energy and projections
The future of renewable energy in the US and UK looks promising. Both countries are expected to continue increasing their renewable energy capacity. The UK is well on its way to creating an electricity system wholly based on renewable and carbon-free sources. In the US, wind and solar are the fastest-growing renewable sources.
Projections and forecasts
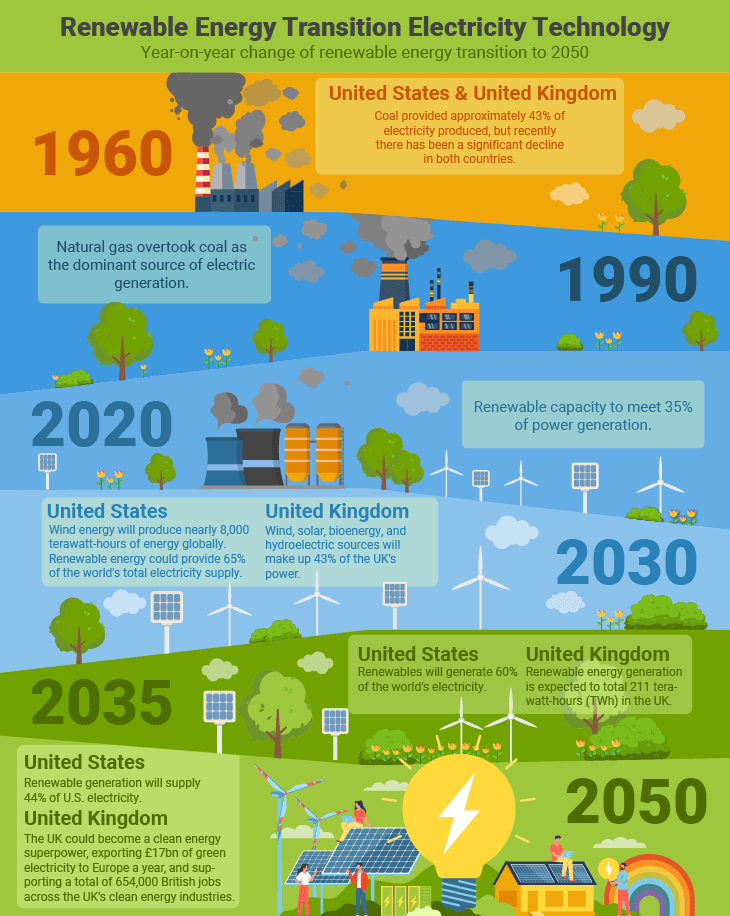
Based on data from IEA, McKinsey and statistics, the table focuses on the renewable energy sources requested: Wind, Solar, Hydro, Biomass, and Geothermal. Here is a comprehensive table presenting the future projection of renewable energy for the United States and the United Kingdom:
| Year | United States | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | Renewable energy resources will make up 30% of the world's electricity, up from 26% today. Solar capacity in the world will grow by 600 GW. Renewable electricity is predicted to grow by 1,200 GW. Hydroelectric power will rise 9%. | Renewable capacity will meet 35% of global power generation. |
| 2025 | Renewable capacity will meet 35% of global power generation | - |
| 2026 | Global renewable-electricity capacity will rise more than 80% from 2020 levels (to more than 5,022 gigawatts). Two-thirds of this growth will come from wind and solar, an increase of 150% (3,404 gigawatts). | - |
| 2030 | Wind energy will produce nearly 8,000 terawatt-hours of power globally, and renewable energy could provide 65% of the world's total electricity supply. | Wind, solar, bioenergy, and hydroelectric sources will make up 43% of the UK's power. |
| 2035 | Renewables will generate 60% of the world's electricity | Renewable energy generation is expected to total 211 terawatt-hours (TWh) in the UK. |
| 2050 | Renewable generation will supply 44% of US electricity. | The UK could become a clean energy superpower, exporting £17bn of green electricity to Europe annually and supporting 654,000 British jobs across the UK's clean energy industries. |
Emerging trends and potential disruptions
Several emerging trends could shape the future of the renewable energy industry. These include:
- Advanced Photovoltaics: Innovations in photovoltaic (PV) technologies focus on high-efficiency solutions.
- AI and Big Data: These technologies enhance renewable energy by facilitating applications like predictive maintenance and smart management.
- Distributed Energy Storage Systems: These systems add flexibility and stability to renewable energy.
- Green Hydrogen represents the results of years of renewable energy research and is a promising avenue for future energy solutions.
- Grid Integration: This is crucial for the efficient use and distribution of renewable energy.
Potential disruptions to the renewable energy transition could arise from geopolitical conflicts, energy security concerns, macroeconomic impacts, and the North-South divide. The current global energy crisis also brings new opportunities and challenges for renewable energy.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?