- GreenMatch
- Plastic Bottle Recycling: Statistics & Trends
Plastic Bottle Recycling: Is It A Solution to the Global Plastic Waste Problem?

In our modern world, plastic water bottles have become ubiquitous in our daily lives. They are convenient, portable, and provide a means of hydration on the go. However, plastic water bottle recycling is a significant global issue due to plastic bottles' massive production and consumption.
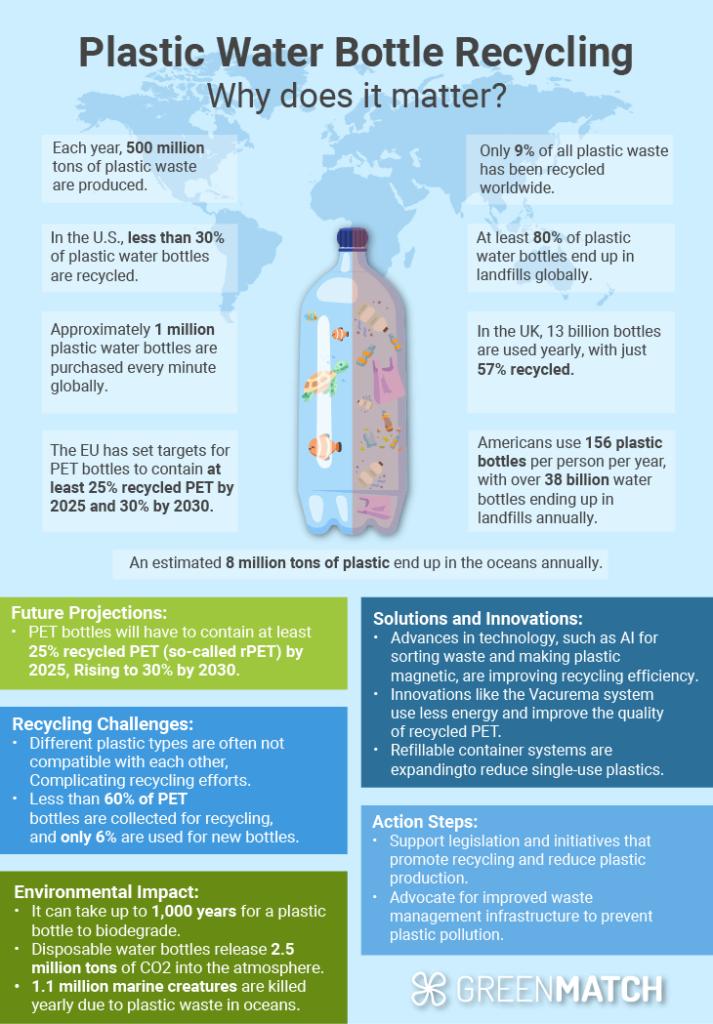
Around 500 billion plastic bottles are used worldwide yearly, with 35 billion empty water bottles discarded in the US alone. However, only 12% of these bottles are recycled, and 91% of the world's plastic bottles are not recycled.
The global plastic bottle recycling industry was valued at £3.2 billion in 2022 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2023 to 2031, reaching £5.1 billion by the end of 2031.
Regarding recycling rates, Germany leads the world with a recycling rate of 56.1%. Other countries with high recycling rates include Austria, Slovenia, the Netherlands, Denmark, Belgium, Luxembourg, Switzerland, and Italy. Norway stands out for its recycling rate of PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastic bottles at 97%.
In the US, PET bottles account for approximately 65% of post-consumer bottles recovered for recycling. However, only about 30% of plastic bottles and jugs are recycled.
The recycling infrastructure plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of plastic bottle recycling. Well-established collection systems, sorting facilities, and recycling plants enable efficient processing of plastic bottles.
Technological advancements and innovations in recycling technology, such as chemical recycling and advanced sorting systems, have the potential to significantly increase the efficiency and quality of plastic bottle recycling.
Despite these efforts, much plastic waste remains in landfills or the natural environment. For instance, 79% of plastic ever produced still sits in landfills or the natural environment.
The Importance of Plastic Water Bottle Recycling
Recycling plastic water bottles is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps drastically reduce the amount of environmental litter. According to Plastic Oceans, 14% of all litter comprises beverage containers. Moreover, recycling plastic bottles significantly reduces energy consumption.
It is estimated that 75% less energy is consumed for each recycled bottle compared to producing a new one. This process also reduces water consumption, as new water bottles require six times the amount of water they contain to produce.
Recycling plastic bottles also helps to reduce the demand for raw materials, thus protecting natural resources and reducing emissions of heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere. Furthermore, it reduces fossil fuel consumption, as plastic production uses a significant amount of oil.
By recycling, we can also reduce the amount of plastic waste ending up in landfills, thereby reducing the emission of common landfill gases like carbon dioxide and methane.
Rates, Growth and Market Segmentation
The current rates of plastic water bottle recycling and the growth trends in the market are significant indicators of our global efforts towards environmental sustainability.
In 2018, the recycling rate of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) bottles and jars was 29.1%, and the rate for HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) natural bottles was 29.3%. However, by 2021, the total plastic bottle recycling rate had slightly decreased to about 27.2%. Despite this, the recycling rate for single-serve PET plastic bottled water containers has doubled in the last decade to 33%.
The global plastic bottle recycling market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. It is anticipated to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.03% during the forecast period, reaching £5625 million by 2030.
This means the plastic bottle recycling market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5% through 2030. This growth is driven by the rising demand for food & beverages among consumers and the increasing awareness about the environmental benefits of recycling.
| Region | Market Share |
| North America | Dominant |
| Europe | Significant |
| Asia Pacific | Growing |
| Middle East & Africa | Emerging |
| Latin America | Emerging |
Despite the progress, there is still a long way to go. The recycling rates for plastic bottles are still low compared to their usage, and a significant amount of plastic waste still ends up in landfills or oceans.
Market Segmentation
The plastic bottle recycling market can be segmented based on various factors such as types of plastic bottles, applications, geography, and key players. According to the research reports, the market segmentation based on types includes PET, PE, and PP plastic bottles. Each type has unique properties and applications, affecting the recycling process and end-products.
The market is also segmented based on the application, with segments including pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, consumer goods, and others.
Geographically, the market is segmented into key regions such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World, with North America dominating the global market in 2022.
| Product Type | Application |
| PET Plastic Bottle | Chemical |
| PE Plastic Bottle | Cosmetic Products |
| PP Plastic Bottles | Other |
The applications segment comprises chemical cosmetic products. The demand for recycled plastic bottles in various industries, including packaging, textiles, and consumer goods, has fueled the market's growth.
Understanding Recycling Symbols on Plastics
Recycling symbols on plastics play a crucial role in recycling, helping consumers and recyclers identify the type of plastic material and its recyclability. These symbols, typically found on the bottom of plastic products, consist of a number enclosed in a triangle made of arrows, known as the "resin identification code."
Each symbol is represented by a number (1 through 7) enclosed within a triangle of three arrows. This symbol indicates the type of plastic material used and provides guidance on whether the item can be recycled and how it should be processed.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common recycling symbols and what they mean:
| Resin Code | Abbreviation | Polymer Name | Common Uses | Recyclability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PET or PETE | Polyethylene Terephthalate | Beverage bottles, food containers, peanut butter jars | Widely recycled; can be turned into new bottles, polyester fibres, etc. |
| 2 | HDPE | High-Density Polyethylene | Milk jugs, detergent bottles, plastic bags | Widely recycled; can be turned into new containers, pipes, plastic lumber |
| 3 | PVC or V | Polyvinyl Chloride | Pipes, clear food packaging, shrink wrap | Rarely recycled; contains harmful chemicals, used in speed bumps, cables |
| 4 | LDPE | Low-Density Polyethylene | Grocery bags, bread bags, some food wraps | Sometimes recycled, it can be turned into floor tiles, shipping envelopes |
| 5 | PP | Polypropylene | Yoghurt containers, straws, bottle caps | Increasingly accepted in recycling programs; used in signal lights, battery cables |
| 6 | PS | Polystyrene | Disposable coffee cups, plastic food boxes, plastic cutlery | Rarely recycled; used in egg cartons, take-out containers, rulers |
| 7 | Other | Various Plastics (Various plastics, including acrylic, nylon, polycarbonate) | Multi-layer materials, some food containers, sunglasses | Not commonly recycled. Varies; includes plastics like acrylic polycarbonate, which can be recycled |
Key Players in Plastic Water Bottle Recycling
The plastic water bottle recycling industry is critical to global efforts to manage plastic waste and promote sustainability. Innovative companies, supportive organisations, and proactive government initiatives drive this sector.
Understanding the key players in this industry is essential for recognising the progress being made and the challenges that lie ahead. These organisations, companies, and initiatives are making significant strides in managing plastic waste, particularly in recycling plastic water bottles.
Leading Companies and Organisations
Several companies are at the forefront of the plastic water bottle recycling market. These include
- Republic Services: A leader in the U.S. recycling and non-hazardous solid waste industry. A top player in the plastic bottle recycling market, Republic Services is known for its efficient collection, sorting, and recycling processes.
- Stericycle: This company is another significant player in the plastic bottle recycling market, offering comprehensive waste management services. They specialise in waste solutions, including recycling services.
- B&B Plastics: Involved in the recycling of a wide range of plastics.
- Clean Path Recycling: Focuses on recycling PET plastics.
- Custom Polymers: Offers services in both recycling and compounding of plastics.
- Plastipak Holdings, Inc.: A major player in recycled PET (rPET) product production. Plastipak is a global leader in the rigid plastic packaging and recycling industries, with a solid commitment to innovation and sustainability.
- Waste Connections: Provides collection, transfer, disposal, and recycling services.
- Alpack Plastics: Supplies a variety of recycled plastic products.
- Veolia Environnement SA: A global company with operations in waste management, including plastic recycling.
- CarbonLITE: Specialises in processing used plastic bottles into PET pellets that can be used to make new bottles.
- TerraCycle is an innovative recycling company known for recycling hard-to-recycle materials. They offer free programs and work with local communities to prevent and collect river waste.
These companies are complemented by organisations and initiatives that promote recycling and develop infrastructure to support the industry. For example, the International Bottled Water Association (IBWA) encourages the recycling of all bottled water containers and endorses the concept of a circular economy.
Top Recycling Countries
Several countries have established themselves as leaders in plastic water bottle recycling:
- Norway: As of 2018, Norway had a recycling rate of 97% for PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastic bottles, making it a world leader in this field thanks to an effective bottle deposit system.
- Germany: Known for its successful bottle deposit system and high recycling rates. Germany has used a highly successful bottle deposit system since 2003 to help reduce plastic waste. This scheme has proven successful, and many countries seek to emulate it.
- Sweden: One of the world's best recycling systems has a recycling station within 300 meters of any residential area.
- South Korea achieved a 60% recycling rate in 2020 and banned coloured PVC and plastic bottles.
- Rwanda: Became the world's first 'plastic-free' nation with strict enforcement of its plastic bag and packaging ban.
- Austria: Austria has one of the highest recycling rates globally, with a significant focus on plastic bottle recycling
- United States: Over 90% of plastic collected for recycling in North America is processed in North America. This is up from 60% in 2010.
Other countries with their plastic bottle recycling rate
| Country | Plastic Bottle Recycling Rate (%) |
| Norway | 97 |
| Germany | 98 |
| USA | 29.3 |
| UK | 57.6 |
| France | 58.2 |
| Italy | 45 |
| Canada | 9 |
| Japan | 77 |
| Australia | 31.8 |
| South Korea | 54.4 |
Statistics of Plastic Water Bottle Recycling
The global consumption of plastic water bottles is staggering, with approximately 500 billion plastic bottles used each year. In the United States alone, 35 billion empty water bottles are discarded annually, with only 12% recycled. This overconsumption and poor recycling rate have led to significant environmental challenges.
Recycling Rates and Waste Generation
In 2021, the U.S. plastic bottle recycling rate was 28.2%, driven primarily by PET bottles, which had a recycling rate of 28.7%.
In the UK, 61% of all plastic bottles are collected for recycling.
In the UK, approximately 7.7 billion plastic bottles are bought each year.
Americans purchase about 50 billion water bottles annually, averaging 13 bottles per month for every person in the U.S.
The recycling rate of plastic packaging waste in the UK stands at 44.2%, with a target of 55% set for 2030
Regarding waste generation, bottled water production uses 17 million barrels of oil a year.
Environmental Impact
The water bottling process releases 2.5 million tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere annually.
Plastic waste, including water bottles, contributes to the pollution of our oceans, with at least 14 million tons of plastic ending up in our oceans every year.
Disposable water bottle waste kills 1.1 million marine creatures yearly.
| Metric | Value |
| Annual plastic water bottles purchased in the U.S. | 50 billion |
| Annual plastic water bottles purchased in the UK | 7.7 billion |
| U.S. recycling rate | 12% |
| UK recycling rate | 61% |
| Global recycling rate | 9% |
| Annual CO2 emissions from water bottling | 2.5 million tons |
| Annual plastic waste in oceans | 14 million tons |
| UK plastic packaging waste recycling rate | 44.2% |
| UK 2030 target recycling rate | 55% |
| Annual oil usage for bottled water production | 17 million barrels |
Innovations in Plastic Bottle Recycling
has undergone significant advancements and technological innovations, shaping a more sustainable future for the industry. These innovations could revolutionise how we perceive and manage plastic waste. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and circular economy models, the industry is moving towards a more efficient and environmentally friendly approach to plastic bottle recycling.
This field's advancements and technological innovations are promising and enlightening, offering potential solutions to the growing plastic waste problem.
For instance, breakthrough technology is upcycling waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic into polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. This innovative process, developed by a team of A*STAR scientists, transforms PET plastic waste into critical components for safer lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for a more sustainable energy future.
Biorecycling of plastics is another emerging technology that could promote a circular economy. This process uses biological systems to break down plastic into its essential components for reuse, potentially reducing the amount of plastic in landfills.
| Innovation | Description | Potential Impact |
| Upcycling PET plastic | Transforming waste PET plastic into polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries | Creating a circular economy where PET plastic waste is transformed into valuable materials |
| AI in recycling | Using AI-powered cameras and sorting machines to identify and sort different types of plastics | Improving the efficiency of the recycling process and reducing contamination |
| Biorecycling | Breaking down plastic into its essential components for reuse | Promoting a circular economy in which plastic waste is continuously recycled |
| PureCycle technology | Removing colour, odour, and contaminants from polyethylene plastic waste and transforming it into a “virgin-like” resin | Advancing recycling capabilities and creating high-quality recycled plastic |
| Production of PET bottles from post-consumer waste | Producing PET bottles entirely out of post-consumer waste | Making significant strides towards achieving the EU's recycling targets |
Plastic Bottle Recycling Data
| Year | Plastic Bottles Recycled (in millions) | Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction (in tons) |
| 2020 | 500 | 1,200 |
| 2021 | 700 | 1,800 |
| 2022 | 900 | 2,500 |
Innovative Initiatives
Several innovative initiatives are pushing the boundaries of recycling efficiency. For instance, the PureCycle technology developed by Procter & Gamble removes colour, odour, and contaminants from polyethylene plastic waste. It transforms into a “virgin-like” resin, forming the basis for plastic products.
Another notable initiative is the production of PET bottles entirely out of post-consumer waste. This ground-breaking technology integrates two normally kept separate processes, making it a significant step towards achieving the EU's recycling targets.
The Potential for Circular Economy Models
The circular economy concept is gaining traction in plastic bottle recycling. This model aims to keep plastic in a closed loop, preventing it from leaking into the environment and reducing the need to extract more fossil fuels to create fresh virgin plastic.
However, creating a circular economy for plastics presents several challenges. Poorly functioning markets for recycled plastics and the cheaper cost of using fossil fuels as raw feedstocks for most plastics are significant barriers. Despite these challenges, many companies invest heavily in this space, stimulating end markets for recycled material and driving demand.
Challenges in Plastic Bottle Recycling
The plastic water bottle recycling industry faces numerous challenges. However, it has numerous challenges, ranging from technical difficulties to economic constraints.
Technical Challenges
One of the primary technical challenges in plastic bottle recycling is the complexity of sorting different types of plastics.
Plastics are composed of various polymer types, which melt at different temperatures, making it nearly impossible to recycle different plastics together. For instance, PET and PVC must be separated due to their distinct properties.
Moreover, plastic bottles are often contaminated with food residues, rendering them unrecyclable.
Another technical issue is the degradation of plastic quality during the recycling process. Recycled plastics can vary significantly in melt flow due to remaining contaminants and moisture. Furthermore, recycling is energy-intensive, and additional steps such as post-consumer washing increase costs.
Economic Challenges
Economic challenges in plastic bottle recycling primarily revolve around the cost of recycling and the competition with virgin plastics. This is because recycled plastic costs more than new plastic.
In 2019, recycled plastics cost an extra £57 a tonne compared to virgin plastics. The demand for recycled plastic is skyrocketing, but its market is weak since its virgin counterpart is cheaper and of better quality.
The Gap Between Plastic Production and Recycling
Despite the increasing demand for recycled plastic bottles, recycling rates have remained relatively flat for the past decade. Only a fraction of the plastic produced gets recycled: about 9 per cent worldwide and about 5 to 6 per cent in the United States, according to some recent estimates.
The rapid acceleration of plastic manufacturing, which has doubled roughly every 15 years, has outpaced nearly every other man-made material. For instance 2019, the world produced over 450 million tonnes of plastic. However, our recycling capacity is currently unable to handle the amount and types of plastic we produce.
The Future of Plastic Bottle Recycling
The future of plastic bottle recycling appears promising, with trends and predictions indicating significant growth in the market. The challenge of the environmental impact of plastic waste and the growing demand for sustainable practices. This will undermine the continued innovation and effort essential to improve worldwide plastic water bottle recycling rates.
Future Trends and Predictions
The global plastic bottle recycling market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% between 2023 and 2030. The market size was valued at £3.2 billion in 2022 and is forecasted to reach around £5.1 billion by 2031. This growth is attributed to factors such as
- Increasing demand for eco-friendly products
- Government regulations and recycling infrastructure,
- Technological advancements in recycling processes.
Technological Advancements
will play a crucial role in the future of plastic bottle recycling. Innovations in recycling processes, such as chemical and enhanced mechanical recycling, are expected to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of plastic bottle recycling. Additionally, developing new materials and designs that facilitate recycling and reduce the environmental impact of plastic bottles will contribute to the market's growth.
Importance of Continued Innovation and Effort
Continued innovation and effort are essential to ensure the future success of plastic bottle recycling. This includes:
- Developing new technologies and processes to improve recycling efficiency and effectiveness.
- Enhancing collection methods and infrastructure
- Encouraging collaboration between industry stakeholders, governments, and consumers to promote recycling and reduce plastic waste.
- Implementing stringent environmental regulations and policies to drive the adoption of sustainable practices in the plastic bottle industry.
- Investing in education and awareness campaigns to inform consumers about recycling and proper waste disposal.
In conclusion, the future of plastic bottle recycling is promising, with market growth and technological advancements driving improvements in recycling rates and processes. However, continued innovation and effort are crucial to ensure the long-term success of plastic bottle recycling and mitigate the environmental impact of plastic waste.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

