Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get Free quotes from insulation specialists near you

Save money by comparing quotes and choosing the most competitive offer

The service is 100% free and with no obligation
- GreenMatch
- Insulation
- Cold Bridge Insulation
Cold Bridging Insulation: What Is It & How to Solve It

- Cold bridging can account for up to 35% of heat loss in your home, significantly reducing energy efficiency and increasing heating costs.
- Poorly insulated windows and doors, structural features like steel beams, and gaps in insulation at junctions such as roof-to-wall or floor-to-wall connections are common causes of cold bridging.
- Addressing cold bridging requires continuous insulation, upgraded materials, and professional installation to ensure your home stays warm, energy-efficient, and free from condensation-related problems.
Cold bridging, also known as thermal bridging, is a common issue in many homes across the UK that can compromise energy efficiency, increase heating costs, and even cause condensation and mould. These weak spots in your home insulation allow heat to escape or enter more easily, reducing the effectiveness of even the best insulation systems.
For homeowners looking to improve their home insulation in the UK, understanding and addressing cold bridging is essential to maintaining a warm, energy-efficient, and comfortable living space. From identifying problem areas to implementing effective solutions, professional guidance can make all the difference.
If you're ready to upgrade your insulation and eliminate cold bridging, GreenMatch can help. With just a 30-second form, you’ll receive up to four free quotes from trusted insulation specialists near you, ensuring you get expert solutions tailored to your needs. Click below to get started and make your home more energy-efficient today!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



What is cold bridging?
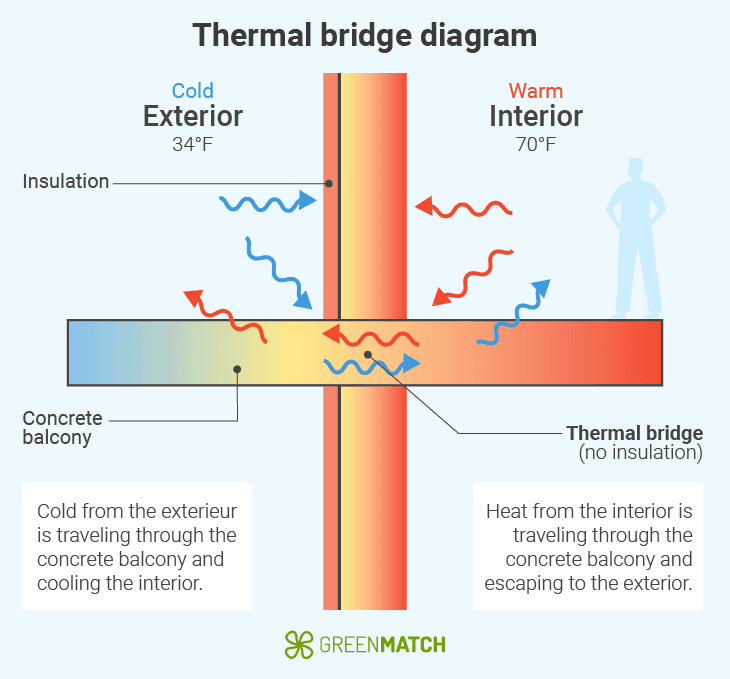
Cold bridging, or thermal bridging, occurs when certain building areas have less insulation than the surrounding structure. These weak points allow heat to transfer more easily in or out, reducing energy efficiency and creating colder surface spots.
Thermal bridges form when there is a break in the insulation, leading to temperature differences between the building’s structure and its insulated areas. Over time, this can cause issues like condensation, dampness, and mould. Cold bridging can be caused by several factors, including:
- Material choice: Concrete, steel, and metal are excellent conductors of heat and can create thermal bridges. These materials transfer heat much faster than insulating materials like foam boards or wool, reducing the effectiveness of the insulation.
- Design flaws: Poor architectural design can result in weak points for heat transfer, such as gaps in insulation, uninsulated areas, or poorly insulated junctions. Examples include window and door frames and connections between walls, roofs, or floors.
- Structural features: Protruding elements, such as balconies or cantilevered sections, can bypass insulation layers and create a direct pathway for heat to escape or enter.
- Inadequate insulation: Poorly installed insulation, including gaps, compression, or misalignment of layers, can lead to thermal bridges. This could be more problematic at corners, edges, and other connection points.
Collaborating with a trusted professional is crucial to preventing cold bridging and ensuring proper insulation in your home. They will ensure that the insulation is installed correctly, maximizing thermal efficiency.
What problems does thermal bridging insulation cause?
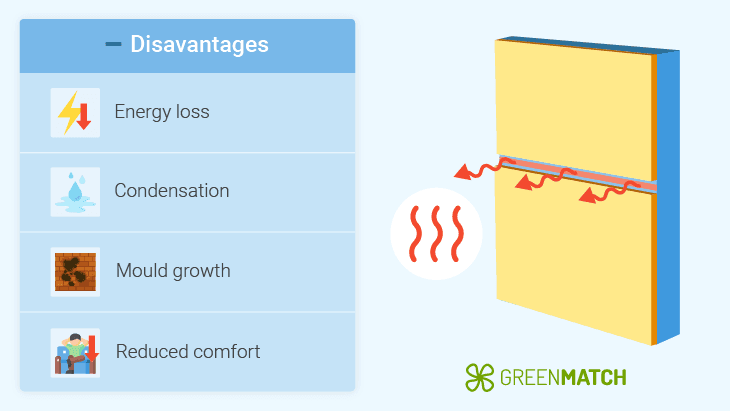
Even small gaps in your insulation can create cold bridges, reducing its thermal efficiency. This not only leads to heat loss in your home but also diminishes the energy savings you could achieve by installing insulation. Here are the problems that thermal bridging insulation can cause:
- Energy loss: Cold bridges increase heat transfer, leading to higher energy bills as heating systems work harder to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. According to EWI Stores, thermal bridging can contribute to up to 35% of heat loss through insulation for walls.
- Condensation and dampness: The colder surfaces created by thermal bridging can cause moisture in the air to condense, especially in high-humidity environments, highlighting the connection between insulation and condensation issues.
- Mould growth: Persistent dampness can lead to mould and mildew, affecting air quality and potentially causing health issues.
- Higher heat in summer: Insulation helps keep your home cool during the summer, but cold bridges reduce its effectiveness, making it harder to maintain a comfortable temperature
- Reduced comfort: As a result of ineffective insulation, the cold spots in a room can make the space feel less comfortable and lead to uneven heating.
Partnering with an insulation specialist helps eliminate issues like cold bridging and significantly boosts your home's thermal efficiency. Plus, by hiring a professional, you could qualify for grants to insulate your home.
Finding the right expert can feel overwhelming and often requires sifting through multiple quotes. That's where GreenMatch steps in—complete our quick 30-second form to receive up to four free quotes from the highest-rated insulation specialists in your area. Click below to discover more!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



Examples of thermal bridging insulation
Thermal bridging occurs when heat transfers more easily through specific building parts due to insufficient insulation or conductive materials. Below are common thermal bridging examples:
- Windows and door frames: Frames around windows and doors, often made of aluminium or other uninsulated materials, act as thermal bridges. Due to their higher thermal conductivity than the surrounding insulated walls, these frames provide a direct path for heat transfer. Poorly installed or uninsulated frames increase heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
- Steel beams: Structural steel beams or supports in walls and ceilings are another classic example. Steel's high thermal conductivity allows it to bypass surrounding insulation, creating cold spots. This leads to significant heat loss and can result in condensation forming around the beam.
- Roof-to-wall junctions: At the junction where the roof meets exterior walls, incomplete or poorly installed insulation can lead to heat escaping through gaps. These junctions are a frequent source of thermal bridging in buildings with insufficient insulation coverage.
- Floor-to-wall connections: When the floor slab connects to walls, gaps in insulation at this junction can turn the concrete slab into a thermal bridge. This transfers heat between the building's interior and exterior, reducing energy efficiency.
- Pipework and ducting: Another example is uninsulated pipes or ducts that pass through insulated walls or ceilings. Metal pipes, in particular, effectively transfer heat or cold, creating localized cold spots and reducing overall thermal efficiency.
Addressing these thermal bridging examples can improve a building's energy performance, reduce heat loss, and prevent condensation-related problems.
How to solve cold bridging insulation

Cold bridging can reduce your home's energy efficiency and lead to issues like heat loss, condensation, and dampness. Here are effective solutions to address it:
- Add continuous insulation: Ensure insulation layers are continuous, covering all junctions, corners, and connections. External wall insulation is particularly effective in minimising thermal bridging across the building envelope.
- Upgrade windows and doors: Replace old ones with energy-efficient options like double- or triple-glazed units with insulated frames. Proper sealing and alignment during installation are crucial to prevent gaps.
- Insulate problematic junctions: Focus on areas prone to thermal bridging, such as roof-to-wall connections, floor-to-wall joints, and window reveals. High-performance insulation materials like foam boards or aerogel are effective in these locations.
- Address structural features: For structural protrusions like balconies and cantilevered elements, use insulated connectors or thermal isolation techniques. Alternatively, redesign these features with thermal performance in mind.
- Seal gaps: To reduce heat transfer, fill gaps in the building envelope using sealants, membranes, or foam insulation. Combine with insulation to create a more airtight and energy-efficient home.
- Work with professionals: Consult experienced insulation specialists or energy-efficiency experts to assess your home and recommend tailored solutions. Professionals ensure proper installation and use of advanced materials to eliminate thermal bridging effectively.
Addressing cold bridging effectively requires the right expertise and materials to deliver long-lasting results. Partnering with professionals can help maximise your energy savings and enhance your home's comfort.
However, finding the right expert can be challenging. That's where GreenMatch comes in—fill out our 30-second form, and we'll connect you with up to four trusted insulation specialists in your area, completely free of charge. Click below to get started!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



FAQ
Thermal bridging insulation refers to materials or techniques designed to minimise heat transfer through weak points in a building’s structure.
Cold bridging occurs when a material with high thermal conductivity allows heat to bypass insulation, creating a direct path for heat transfer.
Cold bridging can be fixed by adding continuous insulation, using thermal breaks, sealing gaps, and addressing problem areas like junctions or frames.
Signs of cold bridging include cold spots on walls, condensation, dampness, and potential mould growth in affected areas.
Thermal bridging can account for up to 35% of total heat loss in poorly insulated buildings.

Caoimhe is an experienced content writer and researcher who is passionate about providing accessible information to every reader. With a background in English literature and Sociology, she combines the two disciplines to create cohesive, well-thought-out, and well-informed pieces.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



