Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get Free quotes from insulation specialists near you

Save money by comparing quotes and choosing the most competitive offer

The service is 100% free and with no obligation
- GreenMatch
- Insulation
- Insulation Building Regulations
- Floor Insulation Building Regulations
What Are the Building Regulations for Floor Insulation in the UK?


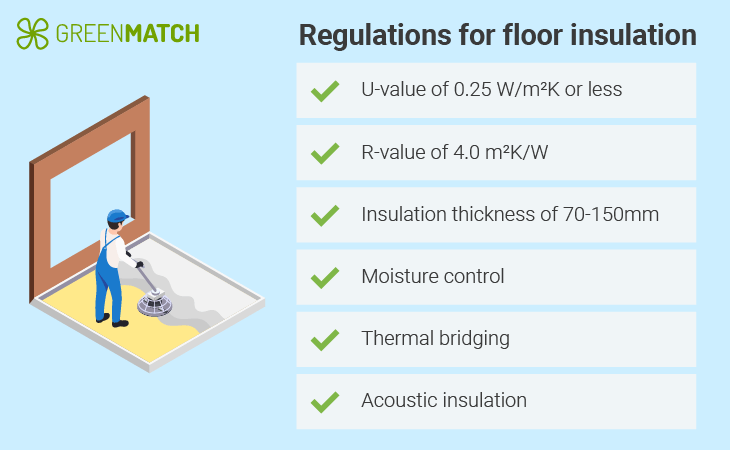
- Floor insulation must meet specific standards related to U-values, insulation thickness, moisture control, and ventilation.
- The required U-value for floors differs by region. For retrofitted floors, England, Wales, and Northern Ireland require an improved U-value of 0.25 W/m²K or lower.
- Scotland has a stricter requirement, with floors needing to meet a U-value of 0.18 W/m²K or lower.
- Non-compliance with building regulations can undermine insulation integrity, leading to costly repairs and penalties. Adhering to these regulations is vital for energy efficiency and insulation benefits.
Floor insulation is fundamental in enhancing buildings' energy efficiency and moisture control. The UK's building regulations and floor insulation standards ensure that floors are insulated adequately to minimise heat loss and prevent moisture-related issues.
These regulations vary depending on the type of floor—concrete floors, suspended floors, or specific flooring types like vinyl—and require adherence to thermal performance measures. This guide will detail which regulations to follow when implementing your floor insulation project.
Meeting regulations can be complex, and mistakes may lead to costly rework or poor insulation performance. Hiring a professional ensures compliance with UK standards, improves energy efficiency, and saves on energy bills. Click the button below to receive up to 3 free tailored quotes from trusted experts!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



What are the building regulations for floor insulation?
The UK building regulations specify that all new builds and significant renovations must meet specific energy efficiency standards, which include floor insulation. Specifically, under Part L of the Building Regulations (Conservation of Fuel and Power), the best floor insulation must meet certain thermal performance levels (U-values).
U-value
The U-value indicates how efficiently a floor prevents heat from escaping; the lower the U-value, the slower heat will transfer through the floor, improving energy efficiency. The maximum U-value for floors is set at 0.13 W/m²K for most new builds.
For a ground floor, the U-value should not exceed 0.25 W/m²K, though lower values may be required depending on the type of floor and location to improve energy efficiency. The insulation material and installation method must comply with these regulations to reduce heat loss and improve energy performance.
In England and Wales, floors should ideally achieve a 0.25 W/m²K or lower U-value.
Tip: Building regulations for floor insulation differ depending on the flooring type. Each type—concrete, suspended, and vinyl—has specific insulation requirements.
R-value
When considering the R-value, the R-value measures a material’s resistance to heat flow, with higher R-values representing better insulation properties.
While the building regulations for floor insulation don't explicitly state a minimum R-value, achieving the target U-value generally necessitates an R-value in the range of 3 to 4, depending on the type and thickness of insulation used.
The insulation's R-value will also vary depending on the specific material, with rigid foam boards offering higher R-values per unit thickness than materials like fibreglass or mineral wool.
Insulation thickness
The minimum thickness of floor insulation depends on the insulation material used and the specific U-value requirement you must meet. To provide you with a clear breakdown of the minimum insulation thickness required for different materials, we have compiled the following table:
| Insulation material | Approximate thickness (mm) |
|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PIR) | 70 - 100mm |
| Expanded polystyrene (EPS) | 70 -1 00mm |
| High-performance foam | 70+ mm |
| Mineral wool | 100 - 150mm |
| Rigid foam boards | 100 - 150mm |
For standard rigid insulation boards, such as polyurethane (PIR) or expanded polystyrene (EPS), the typical thickness required to meet building regulations is around 70-100mm, depending on the material’s thermal conductivity and the type of floor construction. However, in some cases, thicker insulation may be necessary to achieve better thermal performance.
Echoing this, the Energy Savings Trust adds that to meet this standard, you'll typically need at least 70mm of high-performance foam insulation. Mineral wool or rigid foam boards with at least 100-150mm thickness are commonly used to meet regulations. However, the thickness required will depend on the floor's type, shape, and size.
The thickness may vary for retrofitting projects due to space constraints, but ensuring the floor meets the U-value requirement is mandatory under the floor insulation building regulations.
Moisture control
Moisture control is critical in floor insulation, particularly in floors situated over unheated spaces or in contact with the ground. The building regulations floor insulation mandates using a DPM or vapour control layer to prevent ground moisture from entering the building, which can cause dampness, mould, or structural damage.
According to the UK Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Energy’s guide to solid floor insulation, solid concrete floors typically have a DPM beneath the insulation to prevent moisture ingress.
Also, the insulation is often rigid and vapour impermeable, requiring a moisture-closed strategy. Particular attention should be given to thermal bridging, particularly at the edges of the floor and where the floor meets walls or other structures.
In suspended floors, especially timber floors, a vapour barrier is crucial to protect the wooden joists from moisture and condensation, which can lead to rot and structural failure. We recommend using additional barriers in high-moisture areas like basements.
Thermal bridging considerations
One important factor often overlooked in floor insulation is thermal bridging. This occurs when materials with poor insulating properties, such as steel or concrete beams, create a "bridge" for heat to escape. To comply with building regulations for floor insulation, it is essential to minimise thermal bridging. This can be done by:
- Continuously insulating the floor structure with materials that wrap around or break the conductive pathway.
- Ensure that junctions between the floor and walls or around doors and windows are well-sealed to avoid cold spots.
Part L of the UK Building Regulations emphasises the need to address thermal bridging in all forms of insulation adequately to meet energy efficiency targets. To prevent localised heat loss and condensation, thermal bridges should be minimised at junctions, edges, and corners of solid floors. Installing an insulated perimeter upstand can help reduce these risks.
Acoustic insulation
While thermal insulation is the primary concern for floor insulation, acoustic insulation is also important in multi-storey buildings or between flats in shared properties. For multi-storey buildings or flats, insulation between floors is essential for thermal and acoustic purposes, reducing heat loss and limiting noise transmission between separate living spaces.
The Building Regulations Part E addresses soundproofing between floors to prevent noise transmission between different spaces. Occasionally, floor insulation systems designed for thermal purposes also help reduce sound transmission.
For floors with underfloor heating, the type of insulation used should support thermal resistance and reflect heat upwards into the living space. Common products include thermal insulation boards designed to work efficiently with heating systems.
Choose the right insulation to ensure your underfloor heating system operates at peak efficiency. In just 30 seconds, fill out our quick form, and you'll receive up to 3 free quotes from trusted professionals. Don’t wait—maximise your comfort and savings today!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



Additional considerations
In addition to the core requirements for thermal performance, several other important factors must be considered when ensuring compliance with UK building regulations for floor insulation.
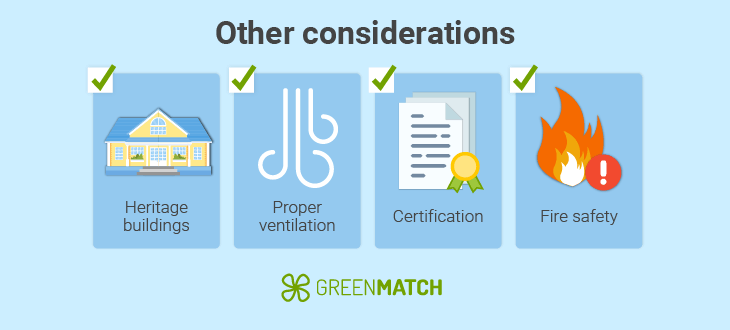
- Heritage buildings: Part L1B may necessitate alternative insulation methods for older or heritage-listed buildings to maintain their character.
- Ventilation requirements: Proper ventilation prevents condensation and rot, especially for suspended floors. Ventilation systems must comply with Approved Document F to ensure moisture control and adequate airflow, especially when insulation reduces natural ventilation.
- Compliance and certification: Floor insulation materials must comply with British Standards (BS EN 13163) for fire safety, moisture resistance, and energy efficiency. An SAP (Standard Assessment Procedure) calculation may be needed to prove energy efficiency, especially for Building Control approval.
- Fire safety: Under Part B of the UK Building Regulations, insulation must meet fire resistance ratings in multi-storey or shared buildings. It must not contribute to fire spread, and fire-resistant boards may be required, particularly between timber floor joists.
How to meet building regulations for floor insulation
To comply with UK building regulations for floor insulation, follow these key steps:
- Achieve the required U-value: Floors should not exceed a U-value of 0.25 W/m²K (or lower). Select insulation materials with low U-values and apply them at the correct thickness to meet requirements. Aim for a 0.25 W/m²K or lower U-value for new builds, while retrofits may vary slightly.
- Calculate insulation thickness based on the R-value: If you have limited space, use higher-performance materials like rigid foam boards.
- Select the right insulation material: Choose appropriate materials for the floor type (e.g., concrete, suspended timber, vinyl). For concrete, use rigid foam boards or insulation below the slab. For suspended floors, install insulation between joists with a vapour barrier. Finally, for vinyl flooring, ensure proper underfloor insulation for thermal comfort.
- Minimise thermal bridging: Ensure continuous insulation across the floor and seal junctions to prevent heat loss through thermal bridges (e.g., at edges, joists, and door thresholds).
- Ensure moisture control: Install a damp-proof membrane (DPM) in concrete floors to block ground moisture. Use a vapour control layer on suspended floors and ensure proper ventilation in the subfloor space. For high-moisture areas like basements, use additional barriers.
- Comply with fire safety standards: Use fire-resistant materials as Part B of the Building Regulations requires. Ensure insulation meets British Standards (BS EN 13163) and does not promote fire spread.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation, especially on suspended floors, to prevent condensation and rot. Follow Approved Document F to maintain moisture control and air circulation.
- Use certified products and documentation: Use certified insulation products, comply with British Standards, and prepare a SAP calculation to prove energy performance compliance. Keep documentation ready for Building Control inspections.
Consult a professional to ensure your floor insulation meets regulations and maximises energy efficiency. They’ll assess your floor type and provide the best solutions for long-term savings and peace of mind.
Ready to insulate your floors? Let GreenMatch UK simplify the process of finding insulation specialists. Just fill out our quick 30-second form, and you’ll receive up to three free quotes from reliable professionals in your area. Click the button below to get started!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



FAQ
UK Building Regulations (Part L) require floors to meet a maximum U-value of 0.25 W/m²K to improve energy efficiency. The type of insulation and installation must comply with these standards to reduce heat loss. This applies to new builds and significant renovations.
The minimum thickness varies, but for materials like PIR or EPS, it typically ranges from 70-100mm to meet building regulations. The required thickness depends on the material’s thermal conductivity and the type of floor.
Yes, 100mm of insulation is generally sufficient for most floors using high-performance materials like PIR, achieving U-values around 0.22-0.25 W/m²K. However, specific calculations may be needed to ensure compliance with regulations.

Nicole Bea Kerr is a content writer for Greenmatch, leveraging her experience in B2B journalism and editing. She is interested in bringing more awareness to sustainability through informative narratives.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

