- GreenMatch
- Green Hydrogen: The Key To Clean Energy?
Green Hydrogen: The Key To Clean Energy?

As we search for cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, one solution has emerged as a potential game-changer: green hydrogen. This remarkable power source can be created through renewable sources and can power many areas, from transport to home heating.
For a long time, we've heavily relied on fossil fuels for our energy needs, which has resulted in harmful emissions and climate change. However, with the development of technology, we could end the need for fossil fuels altogether.
But what exactly is green hydrogen, and how does it differ from the fuels we've used for centuries? In this article, we'll look at how it is made, ask whether there are disadvantages to producing a new fuel source and whether this could be the key to a more sustainable future.
What is green hydrogen, and how is it made?
Hydrogen (or H2) is the most abundant chemical in the universe. It is present in most organic matter, including plants, water, and humans. As a single element, hydrogen is a colourless, non-toxic, highly combustible gas that can be used as a power source.
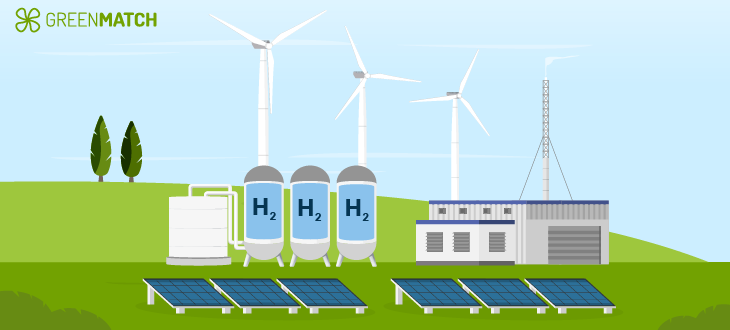
Hydrogen can be artificially created using power sources such as natural gas or nuclear power. These, however, develop significant emissions. By using renewable sources, such as solar energy or wind power, these emissions can be avoided, which makes 'Green Hydrogen'. Also known as sustainable hydrogen, green hydrogen is produced through electrolysis. This method removes hydrogen from water, which doesn't generate harmful pollutants, making it a clean and environmentally friendly energy source.
Step-by-step green hydrogen production
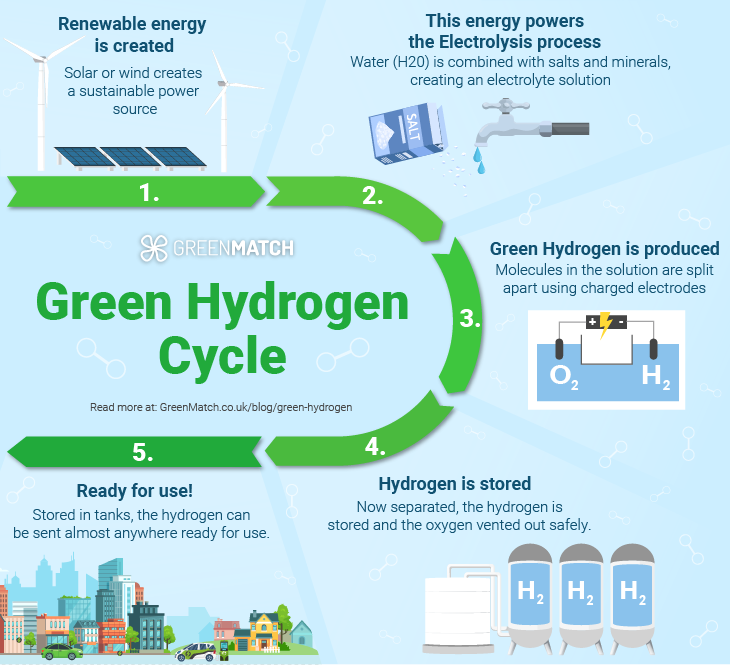
Here is a step-by-step process for making green hydrogen:
1. Preparation of Electrolyte:
The process begins with water (H2O) containing added salts and minerals, known as an 'electrolyte solution'. The salts and minerals are used because they can conduct electricity.
2. Electrodes and Power Source:
Two electrodes, typically made of conductive metal like platinum, are immersed in the electrolyte solution. These electrodes are connected to a direct current power supply, such as wind turbines or solar panels.
3. Electrolysis:
When the power supply is turned on, an electrical current flows through the water. This current causes a chemical reaction to occur, leading to the separation (dissociation) of water molecules into their essential elements: oxygen (O2) and hydrogen (H2).
4. Oxidation-Reduction Reaction:
The electrolysis process involves a reaction caused by the influence of electricity. This reaction creates pure hydrogen gas (H2) and oxygen gas (O2) at one electrode. This process is known as the oxidation-reduction reaction.
5. Collection and Use:
The generated hydrogen can be collected and used as a clean, sustainable fuel source for various applications. At the same time, the oxygen released during the process can be safely vented into the atmosphere without causing any environmental harm.
By using renewable energy sources to power the electrolysis process, the production of green hydrogen becomes entirely free from carbon dioxide emissions. With this new fuel showing possibilities of being highly efficient and sustainable, could this be the key to replacing fossil fuels and reducing global warming?
Blue hydrogen vs green hydrogen
Hydrogen can be classified into different colour categories, depending on how it is produced. Grey hydrogen, for example, is created using fossil fuels and is most commonly used. However, This is considered the most harmful method of producing hydrogen, as it emits the most greenhouse gases.
Blue hydrogen is considered a lower carbon option despite using natural gas. Whilst the process doesn't avoid harmful emissions, it does use methods to 'capture' the greenhouse gases it creates (in this case, carbon dioxide) by storing them rather than releasing them into the atmosphere.
Blue hydrogen may be considered a better alternative to grey hydrogen, but the benefits differ significantly from green hydrogen.
The central aspect that separates blue and green hydrogen is its energy source. Natural gas is a fossil fuel, which is a finite resource. Its extraction for use as fuel causes methane (a potent greenhouse gas) to leak into the atmosphere. Despite the method used to create blue hydrogen, successfully capturing emissions being created, using natural gas is still a harmful production method.
In comparison, green hydrogen uses a renewable energy source, such as solar rays or wind power. This means that the energy source is renewable but also emissions-free and sustainable.
Is a green hydrogen system the key to a sustainable future?
The potential of green hydrogen as a fuel source is becoming an increasingly popular concept, with many sectors agreeing that it could replace their reliance on fossil fuels.
Decarbonising is difficult for sectors such as transport, steel and chemical production. Finding low-carbon options for processes built upon fossil fuels is the biggest challenge. For example, high temperatures are needed in steel making, usually from coal burning. Similarly, many chemical industries' products come directly from fossil fuels.
For these industries, an alternative option like green hydrogen can help bridge the gap to becoming low-carbon or even carbon-neutral. One way it can support this is through its ability to be used as an energy storage system.
Hydrogen can be stored, allowing large quantities of clean energy to be available on demand. This can give users independence from the grid and offer a renewable choice during peak production hours.
Hydrogen can be stored in fuel cells to generate electricity, as a gas in high-pressure tanks, or as a cryogenic liquid. Its versatility gives it even more significant potential to support more companies and industries in converting to renewable options.
As an alternative fuel source, hydrogen is already being trialled and promoted around the globe. The concept of a hydrogen gas blend to fuel gas boilers is also on the horizon for the UK, and many boiler manufacturers have already adapted their technologies to use hydrogen.
Hydrogen is also a versatile product which, with the right equipment, can be used in different ways. For example, green hydrogen can emit high-temperature heat that can be used for large industrial applications. There are also opportunities to turn hydrogen into electricity using fuel cells as a direct power source.
Here are some ways green hydrogen can be used to help create a more sustainable future:

Advantages and uses
-
Zero Emissions:
Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar, resulting in minimal to no carbon emissions during production. Green hydrogen is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
-
Versatility:
Green hydrogen has a wide range of potential applications. It can be used as a clean fuel for transportation, energy storage, and various industrial processes. This versatility positions it as a solution for decarbonising multiple sectors, including heavy industry and transportation.

-
Home heating:
Due to its ability to reach very high temperatures, green hydrogen is an encouraging fuel option for home heating, particularly as some other renewable alternatives can't achieve the same temperatures.
-
Energy Reserves:
Hydrogen can store excess energy from renewable sources when they are abundant (e.g. on a sunny or windy day) and release it when needed. This ability to store and transport energy can help stabilise the electricity grid and make renewable energy sources more reliable.

-
Reduced Fossil Fuel Dependence:
By replacing hydrogen from fossil fuels ('grey hydrogen'), green hydrogen helps reduce our dependence on non-renewable resources. This transition is essential for achieving sustainability goals.
- Global Commitments: Many countries and organisations have committed to achieving carbon neutrality and reducing emissions. Green hydrogen aligns with these goals and will likely play a significant role in meeting these commitments.
We now know that green hydrogen is a very versatile energy source and can have many applications across several industries. However, some speculation surrounds the challenges of implementing this new fuel source. Below are some of the points which still need to be considered.
Challenges and disadvantages

-
High Costs:
Currently, the production of green hydrogen is relatively expensive compared to hydrogen produced from fossil fuels. The costs are primarily associated with the production of renewable electricity and the efficiency of the electrolysis process. Lowering production costs is crucial for making green hydrogen systems more competitive.
-
Energy Intensive:
The electrolysis process, which produces green hydrogen, requires significant electricity. Scaling up production while ensuring a stable, affordable renewable energy supply can be challenging.

-
Infrastructure Development:
Building the necessary infrastructure for green hydrogen systems, storage, and transportation is substantial. This includes the construction of electrolysers, pipelines, and refuelling stations. It requires significant investments and planning.
-
Transportation and Storage:
Hydrogen is more challenging to transport and store than fossil fuels. It requires high-pressure or cryogenic storage, which can be complex and costly.

-
Intermittency of Renewable Energy:
Green hydrogen production depends on a stable and abundant renewable energy supply. The intermittency of sources like wind and solar power can affect the consistency of green hydrogen production.
-
Safety Concerns:
Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, which raises safety concerns, especially in transportation and storage. Safety measures and standards must be established and adhered to.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development and increased investments in green hydrogen technology will address many of these issues.
Emerging trends and innovations for
Green hydrogen is changing the game in the search for clean energy. Let's check out the newest trends and breakthroughs pushing this cool field forward.
- Carbon intensity evaluation: The industry is doing more than just using simple colour codes (green, blue, grey) to figure out the real carbon footprint of making hydrogen. This change helps measure the environmental impact and promotes sustainable ways of doing things.
- Electricity-free electrolysis: New ideas like electrolysis without electricity make green hydrogen production more productive and cheaper. Methods such as photoelectrode modules and the E-TAC process eliminate the need to use electricity from renewable sources, which cuts costs and makes things less complicated.
- Market growth: The green hydrogen market is taking off. It exceeded £5 billion in 2024, and people think it'll grow by more than 31% yearly until 2032. Big companies like Siemens Energy and Air Liquide invest much money into this. They're working on huge projects and making the setup better.
- Advanced electrolysers: New electrolyser tech, like Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) and Solid Oxide Electrolyzers, influences boosting productivity and cutting costs. These breakthroughs are key to ramping up production to meet worldwide demand.
- Storage and transport: Creative fixes for hydrogen storage and transport, such as using ammonia to carry it, tackle the problems of hydrogen's low energy density. This makes it easier to move hydrogen over long distances.
Market growth and projections
The UK green hydrogen market is expected to grow at a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.50% from 2024 to 2032. By 2030, the market is projected to reach approximately £11 billion, reflecting the broader global trend where the green hydrogen market size is anticipated to exceed £6.49 billion in 2024.
Government initiatives and investments
The UK government has demonstrated a strong commitment to developing the green hydrogen economy:
- Launched 11 new production projects with an upfront investment of around £400 million over the next three years.
- These initiatives are expected to create more than 12,000 jobs by 2030.
- Announced backing for 7 additional projects with the potential to increase hydrogen production capacity by 800MW.
Private sector involvement
Major companies are playing a crucial role in driving the market forward:
- Global energy services company Baker Hughes has become a partner and investor in Atome Energy, a Leeds-based green hydrogen producer.
- EDF Renewables UK is expanding its Tees Green hydrogen project, aiming to make the North East region a world leader in green technology.
- JCB has invested £100 million in the development of hydrogen engines and unveiled the world's first mobile site hydrogen refueller.
Technological advancements
Innovations in electrolyzer technologies, such as Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) and Solid Oxide Electrolysers, enhance efficiency and reduce production costs. These advancements are crucial for making green hydrogen more competitive with fossil fuels.
By integrating these latest developments and projections, the UK is positioning itself as a global leader in the green hydrogen industry, driving innovation, creating jobs, and contributing significantly to its net-zero ambitions.
Is green hydrogen the key to a clean energy future?
When we consider the future of sustainable, clean energy, it's evident that green hydrogen has the potential to make a huge difference. A fuel source that produces zero emissions is generated from renewable sources and can be used across industries. It is a valuable tool to battle climate change.
Decarbonising industries, such as transport and manufacturing, along with the ability to store hydrogen, gives us greater flexibility and control over our energy processes. We could fuel our homes of the future with entirely renewable energy sources, transport goods emissions-free, and even fuel our planes and ships, all with the power of green hydrogen.
While this is all exciting to imagine, we must also acknowledge the challenges in bringing these ideas to life. Green hydrogen can be expensive to produce and requires new infrastructure and technologies. The road to a hydrogen-based future will have hurdles.
Research and development efforts are continuously underway to enhance the efficiency and reduce the cost of green hydrogen production. As renewable energy sources become more affordable and accessible, green hydrogen's economic viability improves.
Green hydrogen may not be the key to a clean energy future, but it is crucial in creating a sustainable energy mix.

Becky is an experienced SEO content writer specialising in sustainability and renewable trends. Her background in broadcast journalism inspires reliable content to help readers live more sustainably every day.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?