Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Select the energy-efficient solution that fits your needs best

Independent and unbiased, we’ve helped over 12.000 UK homes go green in the last year!

Our service is 100% free and with no obligation
- GreenMatch
- Heating
- Warm Air Heating System
Warm Air Heating System: Costs, Pros & Cons

Warm air heating is a type of heating system that is typically found in older buildings as they’re now being replaced commonly by wet systems. They peaked in the 1960s-70s mainly because they couldn’t keep up with boiler advantages in the UK.
However, with more interest being shown in reducing our carbon footprint, newer warm air heating systems, such as heat pumps, could be the solution. Find out more about warm air heating systems’ costs, pros, cons, and more in this article.
Do you already know that you would like to upgrade to a modern warm air heating system? We found that the trick to finding the best prices for heating systems is by comparing up to 4 quotes from installers near you. Doing this eliminates the risk of overpaying and lets you choose the best deal.
But looking for installers isn’t an easy nor fast process because you need to tediously call multiple installers, ensure they’re properly certified, explain your heating situation, and ask for quotes.
Luckily, GreenMatch can help you save time while searching for installers and money when requesting quotes. Just click the button and answer some simple questions about your heating demands so that you can get quality quotes quickly.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
What Is Warm Air Heating?
Traditional warm air heating, also known as ducted air or dry systems, is a heating system that became largely outdated in the United Kingdom with the introduction of wet systems that use water-filled radiators supplied by hot water from boilers to heat a home.
Currently, homes with warm air heating systems have upgraded to newer air heating systems, such as air source heat pumps in the UK. Some of the biggest advantages of using warm air heating is that it’s a more carbon-friendly, fast and direct way of heating areas that need it.
Because of this, air heating systems are most effective in homes that are well-insulated and can best keep the heat in. Some variations of this system also provide cooling making it advantageous both in winter and summer.
Because of this dual feature, warm air heating systems tend to be used in countries that have extreme temperatures seasonally. Such as in the United States where 90% of homes have some form of a forced air system.
In contrast, boilers have become more popular in Europe because of its cold winters and until quite recently, cool summers. Thus heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems weren’t needed domestically. Now with the impact of global warming making Europe a hot spot, people are starting to see hot summers as something that’s here to stay.
How Does Warm Air Heating Work?
Warm air heating systems typically work by drawing in cool air from the outside using a vent and warming it up by passing it over a gas flame or to a heat exchanger. The warm air is then circulated throughout the entire house through air ducts, vents or grills in each room.
After the warm air gives up its heat to the room, it is returned to the heating unit through pipes. This process is ongoing until the desired temperature is reached.
The overall system is generally managed by a thermostat, but by opening and closing each vent, the temperature of each room can also be controlled. Once the system reaches the set temperature, it will remain in standby mode until the temperature dips below the established limit, at which point it begins to warm the air once more.
An air source heat pump is one of the most popular warm air heating systems that operates with a heat exchanger. How an air source heat pump works is by transferring heat to a coolant that turns into vapour and then gets compressed into hot dense vapour. It is the heat from this vapour that is then blown out through vents by fans to heat a room.
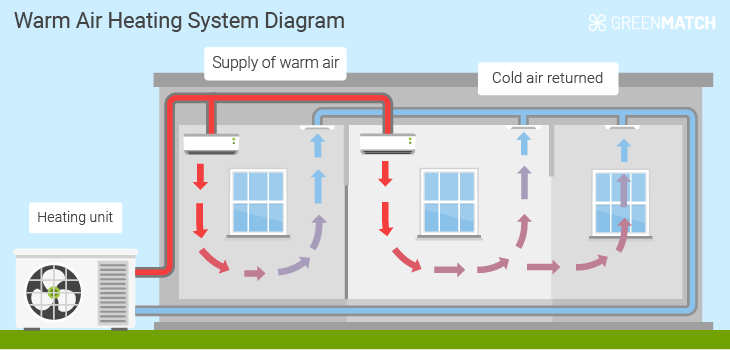
Warm Air Heating System Diagram
How your warm air heating system works can be a complicated process. We’ve simplified the process below in a diagram to show you how a heating unit will circulate the warm air around your home in the winter. What heating unit you have depends on the type of warm air heating system you choose.
Types of Warm Air Heating Systems
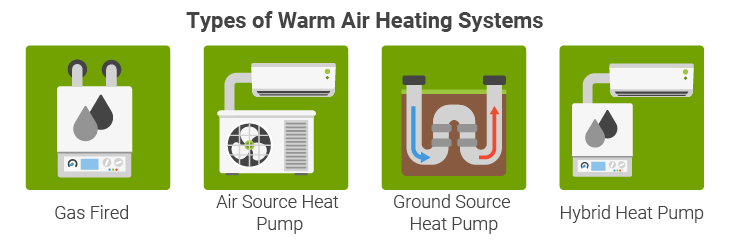
There are 4 main types of warm air heating systems that you can find in homes today. In all cases, they operate through forced warm air being pushed around a duct network using low-power fans. Where they differ the greatest is the method they use to warm the air.
Gas-Fired
Essentially, in a gas-fired warm air system air is drawn in from the outside and heats it over a gas flame. Older gas-fired systems don’t have the capabilities to heat hot water up, but modern models have been designed to do so.
Air-to-Air Heat Pump
Air-to-air heat pumps are a low-carbon heating system that work by essentially using electricity to move air from one place to either cool or warm your home. It transfers heat from one location to another using the principles of vapour compression refrigeration. They are one of the most affordable types of heat pumps to install in your home.
At its simplest, they can be thought of as working like air conditioners, but in reverse. While they are only able to provide heating, you can combine it with other heating systems, such as a boiler, to produce heat for hot water.
Ground Source Heat Pump
Ground source heat pumps that are fitted with geothermal HVAC take advantage of the sun’s energy stored in the ground as heat. In the UK, a few metres beneath the ground surface, the average earth temperature is approximately 8-11°C all year round.
Using pipes which are buried underground, the system essentially works as in-ground pre-heating which draws warm air up through pipes and circulates it through your home's ventilation system.
Hybrid Heat Pump
Hybrid heat pumps combine a heat pump with a boiler to provide home heating and hot water. These systems can alternate between using the boiler’s gas or the heat pump’s electricity to maximise saving on fuel cost and carbon emissions. They work especially when in climates where cooling demands are larger than heating demands.
Hybrid heat pumps pair especially well with homes that require a high heat demand, want to reduce their carbon footprint or are looking to save money on annual bills.
Warm Air Heating VS. Radiators
The main differences between warm air heating and central heating radiators are how they are heated up and how they distribute this heat. Whereas warm air heating is considered a dry system, radiators are considered a part of a wet system.
In a dry system, air is heated up and circulated around your home via vents, ducts, or grills. The warm air typically comes from either a gas-fired unit or a heat pump. In a wet system, water is heated up and supplied to radiators in your home which warm up your home in the winter. In most UK houses with a wet system, the water is typically heated using a gas boiler.
Can You Change Warm Air Heating to Radiators?
Yes, it is possible to change your warm air heating system to a wet system that works with water-filled radiators. In fact, if you have an older home you may have a hot air system as they were popular in the UK in the 1960s and 70s before boiler technology became more advanced and energy efficient.
Swapping a hot air heating system for radiators involves installing a whole new system and removing the components of the old system. You will need to consider that radiators take up space in each room they are in so furniture in your home may need to be repositioned.
Cost of Upgrading Warm Air Heating
If your current warm air heating system is old and you would like to upgrade it to a more modern and energy-efficient warm air heating system, such as an air source heat pump, you could be looking at installation costs ranging from £7,000 to £13,000.
Ultimately, the final cost of upgrading to a new warm air heating system will depend on the size of your home, the number of radiators you need, and the type and fuel you would like to use.
Upgrading your warm air heating system has many long-term benefits. You will see improvements to your carbon footprint and likely lower your annual energy bill because modern heating systems have been designed to be more energy-efficient and cost-friendly.
The first step to getting a heating system is to call installers in your area and ask for quotes about your specific heating situation and demands. For most people, this process can be tedious and time-consuming.
That’s where GreenMatch can help by saving you hours of time, effort, and money.
Using our network of trustworthy partner installers, we can help you find up to 4 tailor-made quotes for the heating system that our certified installers recommend for you. All you need to do to get started is click the button below and answer some questions about your heating demands and we’ll take it from there.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
Is Warm Air Heating Expensive to Run?
The running cost of your warm air heating system will depend mainly on what fuel it uses and how energy efficient your system is. The average house in the UK uses 12,000 kWh of energy for heating annually. While electricity prices have risen, they have not risen as much as gas. With that being said, electricity is still more expensive.
However, you need to consider the energy efficiency of warm air heating systems. For example, an air source heat pump generates, on average, 3kW for every kW of electricity it uses. That’s a 300% efficiency rate. When comparing this with a 92% efficiency standard gas boiler, then the difference in running cost starts to decrease.
Here’s an example of how much an average-sized household will spend on heating if using a warm air heating system that has a coefficient of performance of 3.
| Factors | Calculations Based On |
|---|---|
| Electricity Price | 28.3 per kWh |
| Average COP of an ASHP | 3 |
| Heat Demand of a Medium UK Home | 12,000kWh |
| Electricity Input Required | 12,000/3=4,000kWh |
| Annual Running Cost of ASHP | 4,000*0.17=£1,132 |
Is Warm Air Heating Economical?
Warm air heating is suitable in the UK for smaller properties that are still under construction because it requires a new ductwork/ventilation to be installed. Installing this into a house after it has been fully built is not ideal as it can lead to higher costs and more visible ventilation/pipework.
Therefore, this heating system has definitely found a place in the heating world, but it’s not economically ideal for existing buildings with poor insulation. The reason it hasn’t become more popular in the UK, like it is in other countries, is because systems with cooling weren’t needed in the past and because the advantages and accessibility of boilers have been efficient for UK homeowners.
Warm Air Heating Systems Pros and Cons
Warm air heating systems have many advantages and disadvantages that you should compare before deciding to change heating systems.
Advantages of Warm Air Heating Systems
- Modern hot air heating systems warm your home up quickly and quietly.
- Frees up space in your home as it doesn’t require radiators to be installed making them good for smaller properties.
- Uses less fuel, making them very energy efficient and can cost up to 18% less to run than other heating systems.
- Some warm air systems have an additional filtration system that can remove pollen, dust, and bacteria from the airborne particles.
- Air source heat pumps are low-carbon heating systems that can reduce your home’s carbon footprints because they do not release CO2 into the atmosphere like gas boilers do.
- There are grants available to help cover the cost of installing an energy-efficient warm air heating system.
Disadvantages of Warm Air Heating Systems
- Many air heating systems cannot provide domestic hot water so an additional boiler may be needed.
- Installation of a warm air heating system into an existing house is difficult because the ducts/vents will be visible.
- Air heating systems move dust throughout your home while operating and can be a problem for people sensitive to dust.
- Installing a warm air heating system can come with a high initial cost.
- Because there are few heat pump manufacturers and installers, there is high competition resulting in high costs and limited choices.
If after comparing the pros and cons of warm air heating systems you’ve decided that you would like to upgrade your current heating system to an air heating system, such as a heat pump, then we recommend you first start by comparing installation costs. For most people, this process involves tediously finding local and certified installers and asking for quotes specific to your home.
However, with GreenMatch this process is streamlined as you just fill in a simple form (it takes less than a minute!) and we’ll take it from there by providing you with up to 4 free, tailor-made quotes. To get started, just click the button below.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
Frequently Asked Questions
Despite warm air heating sometimes having a significantly higher initial cost, they are usually cheaper in the long run than a wet system that uses radiators. Although how expensive your warm air system is depends on how energy efficient it is. This is because some hot air systems can reach energy efficiencies between 300% to 500% which can significantly impact the cost.
Whether warm air heating is economical, depends on cost variations that appear when it comes to evaluating elements particular to your heating system, like its age and effectiveness, the quality of your pipes and ducts, and how frequently you utilise the heating system.
Yes, it is possible to change your warm air heating system to radiators. Although radiators may not be fit for all homes so it is important to compare the two systems before installing them.
Yes, modern warm air heating systems have many advantages that make them efficient, quiet, and fast to warm up your home. However, whether an air heating system is good for your home is a different question that you need to consider based on your heating demands.
Warm air heating works by essentially circulating warm air throughout your home using air ducts or vents. When considering installing a warm air heating system, you should consider that different types of warm air heating systems heat the air in different ways that make each type unique.

As a writer with a deep understanding of low-carbon energy systems, Hannah aims to breakdown knowledge barriers and share insights to empower individuals in their pursuit of creating more environmentally conscious homes.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?




