- GreenMatch
- Blog
- Is Nuclear Energy Bad For The Environment? Stats, Trends, And Facts
Nuclear Energy: Environmental Saviour or Silent Threat?

Nuclear energy is also the most reliable energy source, with the highest capacity factor, meaning it can produce maximum power more than 92% of the time. This reliability, combined with its low carbon emissions, makes nuclear power a valuable tool in the fight against climate change.
The United States, for instance, generates nearly 800 billion kilowatt hours of electricity annually, avoiding over 470 million metric tons of carbon each year. This is equivalent to taking 100 million cars off the road.
In emerging markets and developing economies, nuclear power is set to increase by over 5% by 2021, with new reactors led by China coming online in several countries.
However, is nuclear energy safe for the environment? Nuclear energy presents both significant benefits and challenges, making it a complex issue in the context of environmental sustainability.
The production of nuclear energy results in radioactive waste, which can remain dangerous to human health and the environment for thousands of years. This waste's handling, transportation, storage, and disposal are subject to strict regulations to protect human health and the environment.
Nuclear accidents, while rare, can have severe and long-lasting impacts on human health and the environment.
This article delves into the complexities of nuclear energy, exploring its environmental impacts, current trends, and prospects.
What Do We Mean With Nuclear Energy Exactly?
Nuclear energy is released from the nucleus, the core of atoms comprised of protons and neutrons. This energy can be produced in two ways: fission, where nuclei of atoms split into several parts, and fusion, where nuclei fuse.
| Year | Global Nuclear Energy Production (Billion kWh) | Percentage of Global Electricity | CO2 Emissions Avoided (Gigatonnes) |
| 2020 | 2545 | 10% | 60 |
| 2021 | 2672.25 (Estimated) | 10.5% (Estimated) | 63 (Estimated) |
| 2022 | 2805.36 (Estimated) | 11% (Estimated) | 66 (Estimated) |
The nuclear energy harnessed worldwide today to produce electricity is primarily through nuclear fission, while the technology to generate electricity from fusion is still in the research and development phase.
As of the end of 2021, nuclear energy accounted for 10% of the world's total electricity generation.
Nuclear Energy Analysis
| Total world nuclear electricity generation | 2,591 billion kWh |
| Nuclear percentage share of total world electricity generation | 10.1% |
| Total operable nuclear reactors (worldwide) | 440 |
| Top five nuclear electricity generating countries | United States, France, China, Russia, South Korea |
| Largest nuclear power plant | Palo Verde (3,937 megawatts) |
| Number of countries with nuclear power reactors | 33 |
| Uranium expenditures | £54.5 million (approx.) |
| The average price for purchased uranium concentrates U3O8 | is £25.5 per pound U3O8 (approx.) |
| Fuel cost: nuclear vs fossil steam | 0.46 pence/kilowatt hour vs 1.85 pence/kilowatt hour (approx.) |
Environmental Impact of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power plants are vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as changes to air and water temperatures, wind speeds and patterns, and rising sea levels, which can decrease their efficiency.
One of the significant environmental concerns related to nuclear power is the creation of radioactive waste. Managing and disposing of nuclear power plant waste typically represents about 5% of the total cost of electricity production.
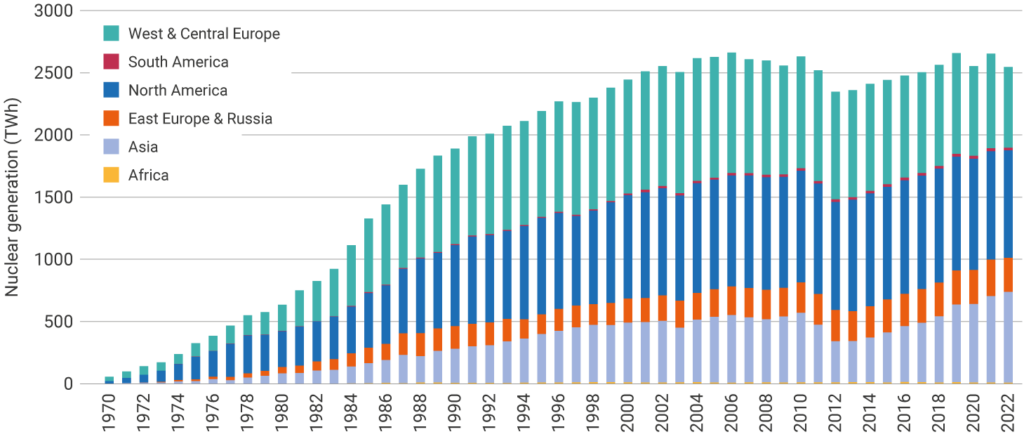
Nuclear energy contributes approximately 10% of the world's electricity, with a higher contribution of nearly 20% in advanced economies. In 2022, nuclear plants supplied 2545 TWh of electricity.
The spread of nuclear technology and nuclear weapons is a threat to national security and the safety of the world.
However, mining and refining uranium ore and making reactor fuel require large amounts of energy, often sourced from fossil fuels.
Nuclear Power Environmental Environmental Impact
| Impact Factor | Description | Potential Consequences |
| Radioactive Waste | Long-lived and hazardous byproducts of nuclear energy production | Health risks, environmental contamination |
| Mining and Refining | Processes involved in obtaining and processing uranium | Environmental degradation, health risks for workers and nearby communities |
| Thermal Pollution | Heat discharged into water bodies from nuclear plants | Adverse effects on aquatic ecosystems |
| Accident Risk | Potential for nuclear accidents and their associated impacts | Long-term environmental contamination, human displacement |
Over the past 50 years, nuclear power has reduced CO2 emissions by over 60 gigatonnes. However, the nuclear fuel cycle, from uranium mining to waste disposal, does have environmental impacts. For instance, each kWh of atomic electricity requires 0.1-0.3 kWh of life cycle energy inputs.
What is so bad about Nuclear Energy for the environment?
Nuclear energy is often lauded for its low greenhouse gas emissions during operation but has significant environmental drawbacks. The production of nuclear energy involves a lifecycle that can harm the environment at several stages:
- Radioactive Waste: The most notorious byproduct of nuclear energy is radioactive waste, which includes spent reactor fuel and other radioactive materials. These substances can remain hazardous for thousands of years and require stringent handling, transportation, storage, and disposal regulations.
- Mining and Refining: The extraction and processing of uranium, necessary for nuclear fuel, can lead to environmental degradation and health risks for nearby communities.
- Thermal Pollution: Nuclear power plants often use water bodies for cooling, leading to thermal pollution, which can negatively affect aquatic ecosystems.
- Accidents Risk: Although statistically rare, nuclear accidents can have catastrophic environmental consequences, as seen in Chernobyl and Fukushima.
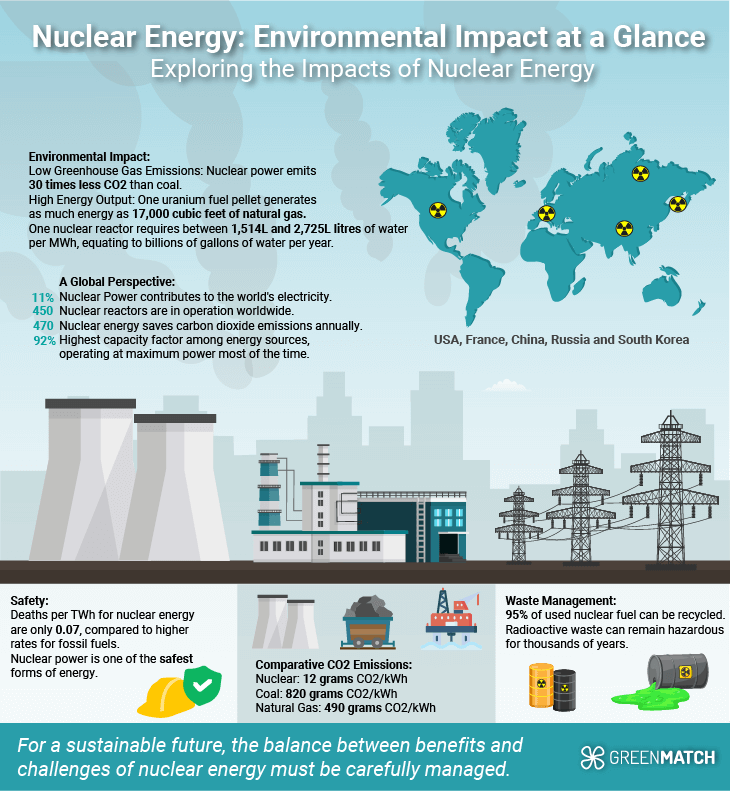
What is the impact of Nuclear Energy?
On the positive side, nuclear reactors do not produce direct carbon dioxide emissions during operation, which makes them an attractive option for low-carbon power generation. These emissions are not negligible, although they are lower than those from fossil fuel-based energy generation.
The impact of nuclear energy on the environment is multifaceted:
- Carbon Footprint: Nuclear power plants do not emit CO2 during operation, making them significant in low-carbon electricity generation. Over the past 50 years, nuclear power has reduced CO2 emissions by over 60 gigatonnes.
- Land Use: Nuclear facilities require less land than some renewable energy sources, potentially reducing habitat disruption.
- Safety Measures: Modern nuclear plants have extensive safety features to minimise the risk of accidents, but the potential for widespread contamination remains a concern.
- Cost: Nuclear energy is also a concern, with new plants being significantly more expensive than renewable energy sources like wind and solar. While nuclear plants have high initial capital costs, their high reliability and capacity factors can make them economically competitive in the long run.
Despite these impacts, some see nuclear energy as necessary for a clean energy future due to its reliability and capacity to produce large amounts of electricity without direct carbon emissions.
Nuclear power will help provide the electricity our growing economy needs without increasing emissions. This is truly an environmentally responsible energy source." - Michael C. Burgess
Top 5 Nuclear Energy in the Largest Economies
The nuclear industry is a significant economic force, supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs and contributing billions to the GDP. For instance, the nuclear industry supports nearly half a million jobs in the United States and contributes approximately £45 billion annually to the U.S. gross domestic product.
| Country | Nuclear Power Plants | Nuclear Energy Production (TWh, 2022) | Total Annual Nuclear Electricity Generation (BkWh) | Nuclear Share of National Electricity (%) |
| United States | 93 | 772 | 789.88 | 19.5 |
| France | 56 | 70% of total electricity | 379.50 | 68.5 |
| China | 51 | Increase by 5% in 2021 | 366.30 | 4.8 |
| Russia | 55 | Increase by 3% in 2019-2020 | 215.75 | 21.0 |
| South Korea | 25 | N/A | 152.33 | 27.7 |
Economic Aspects of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear power is cost-competitive with other forms of electricity generation.
Nuclear power plants are expected to operate for 60 years and even longer, providing a stable energy source with a very low risk of operating cost inflation.
In addition to job creation and economic growth, nuclear power plants may help protect consumers from volatile electricity prices.
Is Nuclear Energy Toxic?
Nuclear energy is not toxic; it's a clean, efficient power source.
Nuclear energy, while a significant source of low-carbon electricity, has a toxic aspect: producing radioactive waste. On one hand, nuclear power plants do not produce direct carbon dioxide emissions, unlike fossil fuel-fired power plants.
This makes nuclear power a significant contributor to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, saving our atmosphere from more than 470 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually.
However, a primary environmental concern related to nuclear power is the creation of radioactive wastes such as uranium mill tailings, spent reactor fuel, and other radioactive wastes. These materials can remain radioactive and dangerous to human health for thousands of years.
Can We Get Rid of Nuclear Energy?
Whether we can get rid of nuclear energy is complex and multifaceted. Nuclear power is cost-competitive with other forms of electricity generation and provides energy stability.
Nuclear power plants may protect consumers from volatile electricity prices. Once power plants are constructed, nuclear energy has meagre variable costs.
Experts have concluded that achieving the deep decarbonisation required to keep the global temperature rise below 2 degrees Celsius would be much easier with an increased role for nuclear power. Considering each country's specific circumstances, deciding to continue or phase out nuclear power involves balancing these risks and benefits.
| Nuclear Energy Facts | |
| Carbon Dioxide Emissions Saved Annually | 470 million metric tons |
| Percentage of Carbon-Free Energy in the U.S. | Over 50% |
| Cost of Managing and Disposing of Nuclear Waste | About 5% of the total generating cost |
| Safety Risks Compared to Coal and Natural Gas | Lower per MWh of supplied energy |
| Role in Combating Climate Change | Crucial for deep decarbonisation |
| Energy Stability | High, with low variable costs once plants are constructed |
Can Nuclear Energy be Recycled?
Yes, nuclear energy can be recycled. This process, known as reprocessing, involves separating the spent nuclear fuel into potentially useful product materials and waste. The separated materials, such as uranium and plutonium, can fuel reactors.
More than 90% of the potential energy in spent nuclear fuel remains even after five years of operation in a reactor, making it a valuable resource for recycling.
Several countries, including Russia, China, France, India, and Japan, have policies to reprocess used nuclear fuel.
Reprocessing can reduce the volume of high-level wastes and the consumption of raw materials. For instance, nearly 96% of used fuel is recyclable, and thanks to recycling, the volume of the most radioactive waste can be reduced by a factor of 5 and its radiotoxicity by a factor of 10 in the long term.
Nuclear Energy Recycling Facts
| Factor | Description | Impact |
| Volume Reduction | Reprocessing spent fuel reduces the volume of high-level waste. | Eases the burden on long-term disposal solutions. |
| Resource Efficiency | Extracts more energy from the original uranium used. | Decreases the need for new uranium mining. |
| Cost | High costs associated with the recycling process. | Economic feasibility is a crucial consideration. |
| Proliferation Risk | Potential security risks due to plutonium separation. | Requires stringent security measures. |
| Technological Advancement | Development of new recycling technologies and advanced reactors. | Could improve the sustainability and acceptance of nuclear power. |
To illustrate the environmental and economic aspects of nuclear energy recycling benefits and impact.
| Factor | Description | Value |
| CO2 Emissions Reduction | CO2 emissions avoided by nuclear power over 50 years | 60 gigatonnes |
| Share of Global Electricity | Nuclear power's contribution to the global electricity supply | 10% |
| Share of Low-Carbon Electricity | Nuclear power's share of low-carbon electricity in advanced economies | 18% |
| Cost of New Nuclear Plant | The potential cost of the Hinkley Point C plant | Up to 46 billion pounds |
| External Costs | of nuclear energy | €18-22/MWh |
| Reliability | Capacity factor of nuclear power plants in 2022 | Over 92% |
Is Nuclear Energy Biodegradable?
Given the nature of nuclear energy and its waste, it is not biodegradable in the traditional sense. Biological organisms cannot break down the waste and remain radioactive for an extended period.
Therefore, while nuclear power has benefits, such as producing zero carbon emissions during operation, the long-term environmental impact of its waste is a significant concern.
| Nuclear Energy Facts | |
| Primary Source | Uranium |
| Energy Production | Nuclear Fission |
| Carbon Emissions | Zero during operation |
| Primary Environmental Concern | Radioactive Waste |
| Waste Management | Storage in specially designed facilities |
| Biodegradability | Not biodegradable in the traditional sense |
Nuclear Waste and Its Impact
The primary environmental concern related to nuclear power is the creation of radioactive waste.
| Nuclear Waste Type | Management Strategy |
| High-level waste | Requires deep and permanent burial. |
| Transuranic waste | Requires specific disposal methods based on risk to human health and the environment. |
| Low-level waste | Managed with less stringent methods due to its lower risk. |
Disposal and Management of Nuclear Waste
The disposal and management of nuclear waste is a significant challenge. Currently, the waste is stored in specially designed facilities, with some countries opting for deep geological repositories.
Nuclear Energy and Climate Change
Nuclear power plants produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Over its life cycle, nuclear produces about the same amount of carbon dioxide-equivalent emissions per unit of electricity as wind and one-third of the emissions per unit of electricity compared to solar.
However, existing nuclear plants are highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Changes to air and water temperatures, wind speeds and patterns, precipitation extremes, and rising sea levels can decrease the efficiency of nuclear power plants.
Is Nuclear Energy Sustainable?
Many experts consider nuclear energy sustainable because it provides much power with minimal carbon emissions. It is a reliable and scalable low-carbon source of energy.
However, the sustainability of nuclear energy is a complex issue with several factors to consider. This waste must be managed carefully, with special regulations governing its handling, transportation, storage, and disposal to protect human health and the environment.
What Are Alternatives to Nuclear Energy?
Alternatives to nuclear energy are varied and cater to different needs and environmental considerations. As a result, there has been a growing interest in exploring alternative energy sources.
Alternatives to Nuclear Energy
- Thorium: Thorium is an abundant alternative to uranium, and the technology to use it has existed since the 1960s. Thorium holds 59% of the world's reserves, primarily in Turkey, India, Australia, and the United States. It produces less waste and is safer than uranium.
- Solar Power: Solar power, harnessed through solar panels, is abundant, inexhaustible, and arguably the best-known alternative energy source. It is the best alternative energy source, and solar panels can convert sunlight into electricity.
- Natural Gas: Natural gas is another good alternative to uranium and oil. It emits less carbon dioxide and can be used as transport fuel. And advancements in technology have made it possible to tap into large reserves of natural gas.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen burns clean and is three times more efficient than a gasoline-powered engine. It can be used along with a fuel cell to provide transport. It can be produced from various sources, including biomass, fossil fuels, or electrolysing water.
- Renewable Energy: This includes wind energy, solar energy, hydroelectricity, biomass energy, and geothermal energy.
Is It Better Than Alternatives?
While nuclear power is reliable and produces no direct carbon dioxide emissions, it is not without its challenges. On the other hand, alternatives like thorium, solar power, natural gas, and hydrogen offer cleaner and safer options.
| Energy Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Nuclear Energy | High capacity factor, No direct CO2 emissions | Creation of radioactive waste, High construction cost |
| Thorium | Abundant, Safer than uranium | Technology not widely adopted |
| Solar Power | Abundant, Inexhaustible | Dependent on weather conditions |
| Natural Gas | An excellent alternative to uranium and oil | Fossil fuel Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions |
| Hydrogen | Burns clean, More efficient than gasoline | Production methods can be energy-intensive |
| Renewable Energy (Wind, Solar, Hydroelectricity, Biomass, Geothermal) | Low greenhouse gas emissions, Combat climate change | Reliability can be affected by weather conditions |
Comparison with Nuclear Energy
When comparing nuclear energy to its alternatives, several factors come into play:
- Reliability: Nuclear power is considered more reliable than renewable sources like wind and solar because it can provide continuous power regardless of weather conditions.
- Emissions: Nuclear energy is one of the cleanest sources of energy in terms of greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Safety: Modern renewable and nuclear power sources are much safer and cleaner than fossil fuels.
- Economic Factors: The levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for nuclear power can be competitive with other clean energy options, especially when considering the costs of extending the life of existing reactors versus building new plants.
- Land Use: Nuclear power plants require less land than renewable sources like solar and wind farms.
- Waste: Nuclear power generates long-lived radioactive waste, a disadvantage compared to renewable energy sources that do not produce such waste.
- Integration with Renewables: Nuclear power can ease the technical difficulties of integrating renewable energy sources into the grid and help lower the overall cost of a clean energy transition.
Statistics, Facts and Figures About Nuclear Energy
Globally, nuclear energy provides about 30% of the world's low-carbon electricity.
Nuclear power plants operate in 32 countries. The largest nuclear electricity producer is the United States, followed by China.
France gets up to around 70% of its electricity from nuclear power, the highest share globally.
The United States, with 93 operable nuclear reactors, generated 772 billion kilowatt hours of electricity in 2022, providing nearly 20% of the nation's power.
In the United States, nuclear energy costs 0.61 cents/kilowatt hour, compared to 2.46 cents/kilowatt-hour for fossil steam.
China has the fastest-growing nuclear power program, with 16 new reactors under construction.
As of 2023, there were about 450 commercial nuclear power reactors operable.
In 2022, nuclear plants supplied 2545 TWh of electricity, down from 2653 TWh.
As of 2024, the U.K. has 15 operational nuclear reactors, which generate just under 20% of the country's electricity.
A survey conducted by the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS) in March 2021 showed that 38% of respondents supported nuclear power, with 17% against and 45% neutral.
Here are some key facts and figures about nuclear energy:
- Nuclear power plants do not emit greenhouse gases while generating electricity.
- Nuclear energy is one of the most reliable sources, with nuclear power plants operating at total capacity more than 92% of the time in 2022
- A typical nuclear reactor produces 1 gigawatt (GW) of electricity.
- Nuclear power plants are used more often because they require less maintenance and are designed to operate for extended periods without interruption.
- Nuclear energy avoids millions of metric tonnes of CO2 emissions. In the UK alone, nuclear power avoided 22.7 million metric tonnes of CO2 emissions in a year.
In conclusion, while nuclear energy has drawbacks, particularly concerning radioactive waste and the potential for accidents, it also offers significant benefits as a low-carbon energy source. This means a reliable power source contributing to the electrical grid's stability.
The debate over its role in a sustainable energy future is ongoing, with valid points on both sides.
As we strive to meet the world's growing energy needs while mitigating the impacts of climate change, nuclear energy will undoubtedly continue to play a crucial role.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

