- GreenMatch
- Blog
- Is Paint Bad For The Environment? Stats, Trends and Facts
Is Paint Bad for the Environment? A Comprehensive Analysis


Paint is ubiquitous in our lives, from the walls of our homes to the finishes on our cars. A fresh coat of paint can transform a room, but have you ever considered the environmental cost of that perfect shade?
Paint doesn't just change the look of our surroundings; it significantly impacts our indoor and outdoor environments. It releases hazardous air pollutants and odours that seriously affect air quality and human health. Substances like Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) can cause eye irritation, breathing difficulties, and other health issues, painting a grim picture of the environmental cost of our perfect shades.
But wait, there's more! This story continues. Aint production also consumes vast amounts of water and energy, leaving a significant environmental footprint. And what about leftover paint? Improper disposal can contaminate soil and waterways, threatening ecosystems and wildlife.
But fear not! This means you can continue refreshing your space or designs. The good news is that the industry is evolving.
Efforts to mitigate these impacts have seen regulations like the 4% tax in China on coatings with high VOC levels, aiming to lower pollution levels. Innovations in manufacturing have introduced eco-friendly solutions like EonCoat, which boasts no VOCs and promotes sustainability.
This article will be your guide to understanding the environmental impact of paint. We'll explore the statistics, trends, and facts that depict the problem.
What do we mean by Paint exactly?
Paint is a mixture we use to add colour, protection, and texture to surfaces. It consists of pigments for colour, binders to hold it together, solvents to make it spreadable, and additives for specific properties.
Over the years, it has evolved from natural substances to complex chemical formulations, offering various applications from artistic expression to industrial protection.
Types of Ingredients in Paint
- Pigments: These are finely ground natural or synthetic particles that impart colour and opacity to paint. Standard pigments include titanium dioxide, iron oxide, and carbon black.
- Binders: Also known as resins, binders are the film-forming component of paint. They can be acrylic, vinyl, epoxy, or oil-based, each providing different durability and finish characteristics.
- Solvents: Solvents dissolve the binder and give the paint consistency in its application. Water is a common solvent in latex paints, whereas oil-based paints may use organic solvents like turpentine.
Understanding these components helps analyse how they interact with the environment and why certain types might be more harmful.
There are three main types, each with unique characteristics and uses.
Types of Paints
- Acrylic: Acrylic paint, known for its durability and resistance to UV light, has a chemical base of liquid plastic polymers and resins. It's pricier and contains more Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), making it less environmentally friendly.
- Latex (Water-based): Latex paint, the most common type, uses water as its binder. It's cheaper, easier to use, and has lower VOC levels, making it a more eco-friendly option. However, it's susceptible to freezing temperatures, rendering it unusable.
- Oil-based: Oil-based paints, with their rich, durable finish, use oil as their binder. They're great for high-impact areas but have high VOC levels and require careful disposal.
Acrylic and oil-based paints pose a higher environmental risk due to their VOC content and the energy-intensive production of their components. Latex paint, while more eco-friendly, still requires careful disposal to avoid environmental harm.
However, the environmental impact is significant and multifaceted. The production, application, and disposal can harm the environment in several ways.
Environmental Impact of Paint
Paint products, especially those based on oil and containing high levels of VOCs, can cause serious health issues through off-gassing as they dry. They also contribute to environmental degradation by forming ozone and peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN), potent greenhouse gases.
The environmental and health impacts necessitate careful consideration of its production, use, and disposal. For instance, the manufacturing process of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2), a standard pigment, is energy-intensive and emits CO2, N2O, SO2, NOx, CH4, and VOCs. Furthermore, paint waste, classified as hazardous due to toxic chemicals like lead, cadmium, and chromium, poses disposal challenges.
Paints can have significant environmental impacts due to their volatile organic compound (VOC) content, heavy metal pigments, resource depletion, waste generation, chemical emissions, and landfill disposal. VOCs contribute to air pollution and health issues, while heavy metals and improper disposal contaminate soil and water.
Paint waste is not only a concern due to its CO2 emissions but also because it takes 700 years to decompose in landfills. For instance, Americans discard more than 65 million gallons annually. Moreover, the traditional pigments contain toxic heavy metals that can leach into the soil and contaminate it, posing long-term health risks.
| Paint Type | VOC Content (g/L) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Oil-based | 380-550 | High |
| Latex | 50-150 | Moderate |
| Low-VOC | <50 | Low |
What is the impact of paint?
The environmental impact is vast and multifaceted. To provide a clearer picture, we break down the impact by total annual effect, daily consequences, and per-usage implications.
- Total Impact per Year: Studies reveal that paint is a leading source of ocean microplastic pollution, with 1.9 million tonnes of microplastics entering marine environments annually. This accounts for 58% of all microplastic pollution.
- Impact per Day: Breaking it down, approximately 5,205 tonnes of paint-derived microplastics pollute our oceans daily. In addition, the industry generates wastewater estimated between 75-85 million gallons per day.
- Impact per Usage: Every gallon of paint applied can release 30 grams of harmful VOCs into the air, contributing to indoor and outdoor air pollution. The exact amount varies based on the type and application method.
Top Paint-Producing Countries
The global industry is vibrant, contributing significantly to economies worldwide. Analysing the international landscape of paint production reveals a few key players dominating the market.
The EU-27 countries produced over £11 billion worth of paints and varnishes. Germany is the largest producer, accounting for over 20% of EU production by volume and value. Italy and France followed as the second and third largest producers, respectively.
China's market exceeded £30 billion in 2023 and is expected to dominate globally. India's market is projected to reach £8.8 billion by 2033, driven by construction growth.
These countries not only lead in production volumes but also significantly influence global trends in paint technology.
Major Paint-Producing Countries
- China: As the most extensive producer globally, China accounts for a substantial portion of the world's supply. The country's vast manufacturing base supports various types, from industrial coatings to decorative paints.
- United States: Known for its innovation in paint technology, the US ranks second. American companies are at the forefront of developing low-VOC and eco-friendly paints, reflecting a strong shift towards sustainability.
- Germany: Germany is renowned for its high-quality paint products, especially in the automotive and industrial sectors. German paint manufacturers are leaders in producing durable and environmentally friendly coatings. This is done by developing low-VOC and water-based systems, reducing environmental harm.
- India: With a rapidly growing infrastructure, India's industry is booming. Indian companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices and green solutions.
- Japan: Japan's paint industry is well-known for its technological advancements and high standards in environmental safety. Japanese paints often incorporate advanced materials to reduce environmental impact.
The top paint-producing countries and their estimated annual production volumes:
| Country | Annual Production Volume (Million Litres) | Production Value (£ billion) | Annual Revenue (£ billion) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 15,000 | £30.5 | £34 billion |
| United States | 10,000 | £20.3 | £28 billion |
| Germany | 4,000 | £3.3 | £22 billion |
| India | 3,500 | £2,7 | £15 billion |
| Japan | 3,000 | £1.8 | £18 billion |

*Data sourced from industry reports and environmental studies.
Leading Companies and Their Eco-Friendly Initiatives
- Sherwin-Williams - This company offers a range of low-VOC and zero-VOC products, focusing on sustainable manufacturing practices.
- AkzoNobel - AkzoNobel is committed to cutting carbon emissions and waste to become carbon neutral and 100% renewable by 2050.
- PPG Industries - PPG has developed innovative technologies to reduce their products' energy consumption and VOC emissions.
- RPM International Inc. - RPM's products are increasingly eco-friendly, focusing on reducing the environmental impact of their manufacturing processes.
- Axalta Coating Systems - Axalta is dedicated to sustainability through its "Sustainable Star" program, which includes products designed to minimise environmental impact.
- BASF - BASF's coatings division emphasises sustainable solutions, including water-based and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. The company aims to reduce its carbon footprint significantly.
| Company | Country | Sustainability Goals | Eco-Friendly Products | Energy Consumption Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sherwin-Williams | USA | Low-VOC initiatives | Yes | In progress |
| AkzoNobel | Netherlands | Carbon neutral by 2050 | Yes | In progress |
| PPG Industries | USA | Reduce energy intensity | Yes | In progress |
| RPM International Inc. | USA | Waste reduction | Yes | In progress |
| Axalta Coating Systems | USA | Sustainable Star program | Yes | In progress |
| BASF | Germany | Reduce carbon footprint | Yes | In progress |
Top Companies with an annual revenue as of 2022/2023
| Rank | Company Name | Headquarters | Annual Revenue (2022/2023) in GBP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The Sherwin-Williams Co. | USA | £14.34 billion |
| 2 | PPG Industries | USA | £14.28 billion |
| 3 | AkzoNobel | Netherlands | £10.23 billion |
| 4 | Nippon Paint Holdings Co. | Japan | £8.01 billion |
| 5 | RPM International Inc. | USA | £5.43 billion |
| 6 | Axalta Coating Systems | USA | £3.97 billion |
| 7 | BASF Coatings | Germany | £3.72 billion |
| 8 | Kansai Paint Co. Ltd. | Japan | £3.11 billion |
| 9 | Asian Paints Limited | India | £2.84 billion |
| 10 | Jotun | Norway | £2.28 billion |
Global Paint Market Size and Growth
Oil-Based vs Water-Based Paints: Which is Right for You?
The debate between oil-based and water-based paints is about more than which dries faster or lasts longer. It's also about their impact on our health and the environment.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Based Paint | Water-Based Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Longer (up to 24 hours) | Shorter (1-2 hours) |
| Durability | High | Moderate to High |
| Finish | Glossy | Matte to Satin |
| Odor | Strong | Minimal |
| Clean Up | Requires solvents | Soap and water |
| VOC Emissions | High | Low |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Key Differences
- Drying Time: Oil-based paints take longer to dry, which can be a disadvantage if you're pressed for time. Water-based paints dry quickly, allowing for faster project completion.
- Durability: Oil-based paints offer excellent durability, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. Water-based paints have improved significantly, offering comparable durability with the correct formulation.
- Finish: After a glossy finish, oil-based paints are your go-to. Water-based paints offer a range of finishes, from matte to satin, but achieving a high gloss is more challenging.
- Odour and Clean Up: Oil-based paints emit a strong odour and require solvents for cleanup, posing health risks. Water-based paints have a minimal odour and clean up easily with soap and water.
- Environmental Impact: Oil-based paints release high levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to air pollution and potential health issues. Water-based paints emit fewer VOCs, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
Is Paint Toxic?
Yes, paint can be toxic. Research indicates that exposure to fumes can lead to severe health issues, such as respiratory problems, allergies, and even increased risk of certain cancers.
The Toxic Ingredients in Paint
Paint contains volatile organic compounds (VOCs), heavy metals, and other chemicals. These substances can cause health issues and environmental damage. Here's a quick look at the main culprits:
- VOCs: Cause headaches, dizziness, and respiratory problems.
- Heavy Metals: Lead, cadmium, and chromium can lead to serious health issues.
- Other Chemicals: Formaldehyde and benzene are known carcinogens.
Health Risks from Paint Exposure
- Immediate Effects: Exposure to fumes can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and lung irritation.
- Long-Term Effects: Prolonged exposure, especially in occupational settings, has been associated with higher incidences of various cancers and chronic health issues.
Can We Get Rid of It?
Yes, we can manage paint's impact responsibly. Traditional methods like manual spraying and rolling often lead to significant waste, classified as "hazardous" due to toxic chemicals.
The good news is that alternatives and proper disposal methods exist. Low-VOC, water-based, and natural paints offer safer options. For disposal, drying out and using paint hardeners can prevent harmful chemicals from contaminating landfills.
In the EU, initiatives aim for zero air, water, and soil pollution, pushing for eco-friendly paint. Regulations limit VOC emissions in the US, and manufacturers are developing paints with lower environmental impacts.
How Much Will It Cost?
The cost of removing or disposing paint varies widely based on the method and scale. Here's a quick breakdown:
| Method | Cost Range (per square foot) | Total Cost for 1,200-2,000 sq. ft. Home |
|---|---|---|
| Professional Lead Paint Removal | £6.08 - £11.40 | £7,296 - £22,800 |
| DIY Encapsulation | £0.61 - £1.06 | £732 - £2,120 |
| Professional Paint Disposal | £3.86 - £7.12 | £4,632 - £14,240 |
These costs reflect the price of safely removing lead-based or disposing of hazardous paint waste. Encapsulation offers a more affordable DIY option, while professional removal ensures safety but at a higher price.
Is Paint Biodegradable?
Most conventional, like oil-based and acrylic paints, are not biodegradable. These paints contain synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals, making them resistant to natural decomposition.
On the other hand, eco-friendly, natural-based paint options are available. These include clay, chalk, milk, and natural earth paints. Unlike their conventional counterparts, these break down naturally without causing harm to the ecosystem. They offer a responsible choice for environmentally conscious consumers, allowing them to make a positive impact with their choices.
For instance, a study on acrylic-based paint biodegradation revealed that specific bacterial isolates could degrade acrylic paint, with removal percentages reaching up to 90.08% for lower concentrations.
Biodegradation of Paints
| Paint Type | Biodegradation Rate | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Low | High |
| Acrylic-Based | Moderate-High | Moderate |
| Natural Ingredient-Based | High | Low |
Is Paint Sustainable?
The question of paint's sustainability touches on its production, use, and disposal, which impact the environment.
Regulations worldwide are pushing for greener solutions. For instance, China imposed a tax on high-VOC coatings to encourage the use of waterborne and low-VOC paints. The European Union's REACH and the US EPA's guidelines aim to limit using hazardous chemicals in paints.
Traditional vs Sustainable Paint
| Aspect | Traditional Paint | Sustainable Paint |
|---|---|---|
| VOC Emissions | High | Low/None |
| Resource Depletion | Significant | Reduced |
| Waste Generation | High | Lower |
| Chemical Emissions | High | Reduced |
| Environmental Certifications | Fewer | More Available |
Sustainability Certifications
Several certification programs promote sustainable products. To aid consumers in identifying genuinely sustainable products, several certification programs have been established:
- Green Seal
- EPA Design for the Environment (DfE)
- EU Ecolabel
- Blue Angel (Germany)
- Milieukeur (Netherlands)
These certifications consider VOC levels, manufacturing processes, packaging, and product life cycles.
Can Paint Be Recycled?
Yes, recycling paint is not only possible but also increasingly common worldwide. Recycling programs help reduce environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and repurposing valuable resources.
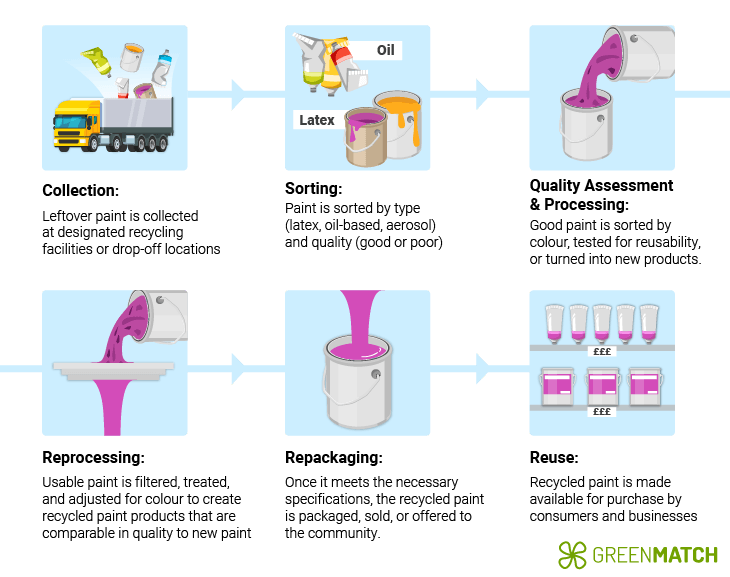
Countries around the world have established recycling programs. In the UK, Canada, and the US, nonprofit organisations like PaintCare facilitate paint recycling. These programs collect millions of gallons annually, preventing harmful environmental impacts and conserving resources.
Recycling centres collect leftover paint from households and businesses. They sort this by type—latex, oil-based, and aerosol—and then process it for reuse. High-quality latex paint, for example, can be turned back into recycled paint products. Non-reusable may be an additive in cement manufacturing or produce biomass fuels.
Paint Recycling by the Numbers
| Country | Gallons of Paint Recycled Annually | Recycling Locations |
|---|---|---|
| UK | 1.5 million | 800+ |
| Canada | 2 million | 1,000+ |
| US | 3.5 million | 1,750+ |
Why Recycle Paint?
Recycling one gallon can save:
| Benefit | Value |
|---|---|
| Energy Saved (per gallon) | 100 kWh |
| Water Saved (per gallon) | 13 gallons |
| CO2 Emissions Reduced (per gallon) | 115 lbs |
| Oil Saved (per gallon) | 1 quart |
| Household Energy Saved (per gallon) | 3 hours |
It also prevents groundwater contamination and air pollution.
Types of Recyclable Paint
Most household paints are recyclable, including:
- Latex/water-based paints
- Oil-based/alkyd paints
- Primers and sealers
- Stains and varnishes
- Aerosol paints
How to Recycle Paint
Most locations accept up to 10 containers of paint or 50 spray cans at a time.
- Check Local Regulations: Recycling options vary by location.
- Prepare Paint for Recycling: Ensure cans are sealed and labelled.
- Drop Off at a Recycling Center: Find a local drop-off site.
- Support Paint Recycling Efforts: Advocate for and participate in local recycling programs.
Environmental Impact Compared to Everyday Things
The industry significantly impacts the environment, with CO2 emissions a significant concern. A 5-litre gallon of paint can result in 13.58 kg of CO2 equivalent (CO2e), a measure of various greenhouse gas emissions in terms of the amount of CO2 that would have the same global warming potential.
For instance, reusing a gallon saves 100 kilowatt hours of energy, which is substantial. The production of titanium dioxide, a standard pigment in paint, contributes to nearly 75% of a tin of paint's carbon footprint.
This figure is startling when compared to everyday items and activities.
To put paint's environmental impact into perspective, let's compare it to everyday activities:
Paint CO2 Emissions vs. Everyday Items
| Item/Activity | CO2 Emissions (kg CO2e) |
|---|---|
| 5-litre Paint | 13.58kg |
| Driving an average Car (60 miles) | 13.6kg |
| London-New York Flight (round-trip) | 986kg |
| UK Household Electricity (annual) | 2,745kg |
As you can see, the carbon footprint of a 5-litre paint gallon is comparable to driving a car for 60 miles or running a refrigerator for a month.
What Are Alternatives to Paint?
Several options offer environmental and health benefits when considering alternatives to traditional paint. These alternatives are gaining popularity due to their eco-friendly properties and innovative features.
Eco-Friendly Paint Alternatives
- Mineral Paints: These are durable and breathable, made from natural ingredients like silicate minerals.
- Milk Paints: Composed of milk protein, lime, and natural pigments, they are biodegradable and non-toxic.
- Clay Paints: Made from natural clay and pigments, they offer excellent breathability and are free from VOCs.
- Chalk Paints: Known for their matte finish, they typically have low VOC content and are easy to use.
- Lime Wash: An ancient paint made from limestone, it's naturally anti-bacterial and mold-resistant.
- Low-VOC and Zero-VOC Paints: These paints have reduced levels of volatile organic compounds, making them safer for indoor use and less harmful to the environment.
- Linseed Oil Paint: Derived from flax seeds, it's renewable and biodegradable.
- Natural Oil Stains: Made from natural oils and resins, they penetrate wood for protection without harmful chemicals.
Is Paint Better Than Alternatives?
Traditional paint is only sometimes better than its alternatives. While it may offer a broader range of colours and finishes, the environmental and health impacts of VOCs and other toxic substances in many conventional paints make eco-friendly alternatives superior to those concerned with sustainability and indoor air quality.
Traditional Paint vs Alternatives
| Alternative | VOC ContentVOC Content (g/L) | Durability | Environmental Impact | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Paint | 450 - 600 | High | High | Medium-High |
| Low-VOC and Zero-VOC Paints | 5 - 50 | High | High | Medium-High |
| Mineral Paint | Low (0 - 50) | High | Low | Medium-High |
| Milk Paint | Zero | Medium | Very Low | Medium |
| Clay Paint | Zero | Medium | Very Low | Medium |
| Chalk Paint | Low | Medium | Low | Low-Medium |
| Lime Wash | Zero | High | Very Low | Low |
| Linseed Oil Paint | Low | High | Low | Medium |
| Natural Oil Stains | Low | High | Low | Medium |
These alternatives are better for the environment and offer unique aesthetic qualities that traditional paints do not. They contribute to healthier living spaces and are often more cost-effective in the long run due to their natural durability.
Statistics, Facts and Figures About Paint
The paints and coatings industry is witnessing substantial market growth and global economic growth. Here, we delve into the key statistics, facts, and figures from industry reports and environmental studies such as Statista, the American Coating Association, and Wikipedia. The focus will consider its environmental impact, usage, production, and more.
Global Paint Production and Consumption
The global paint and coatings industry has grown significantly, with a market size of £117 billion in 2020. This growth reflects an increasing demand across various sectors, including construction, automotive, and industrial applications.
- Asia-Pacific leads in production and consumption, accounting for 55% of global usage.
- Europe and North America follow, strongly focusing on sustainable and eco-friendly paint products.
- The market size is projected to increase from £155.6 billion in 2022 to an estimated £182.7 billion by 2027, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.3%.
- The global market for paints and coatings is segmented into key regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and South America.
- The decorative paints market represented nearly 45% of sales in the industry.
- China is the largest producer, consuming around 60% of Asia-Pacific's paint output.
- The United States, Western Europe, and Japan have mature markets reflecting economic health.
Environmental Impact of Paint
It contributes significantly to environmental pollution, mainly through the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous waste generation.
- Paint is the largest source of microplastics in the ocean, contributing 1.9 million tonnes (58%) annually.
- The architectural sector is the most significant contributor to sea leakage, accounting for 48% of the total.
- Wear and tear from maintaining commercial ships and offshore rigs accounts for 18% of ocean paint microplastics.
- Each oil rig releases around 1,100kg of paint microplastics and 260kg of heavy metals into the ocean yearly.
- Mismanaged waste accounts for over a third (37%) of ocean leakage.
- In North America, paint accounts for 22% of microplastics in the ocean.
- In the Asia-Pacific region, paint contributes 54% of total microplastic leakage.
Paint Waste Management
Effective waste management is crucial in mitigating the environmental impact. However, practices vary significantly across regions:
- Europe leads in paint recycling and waste management initiatives.
- Asia-Pacific and Africa need help with adequate waste management infrastructure.
- Around 12% of the environmental burden comes from wasted, unused paint.
- An estimated 25% of all paint goes unused in the UK domestic market.
- Across Europe, approximately 900,000 tonnes of unused paint are wasted every year.
Innovations and Trends
The industry is witnessing a shift towards green chemistry and sustainable practices:
- The demand for eco-friendly, low-VOC, and water-based paints is rising.
- The bio-based paints and coatings market is expected to reach £5.9 billion by 2027.
Regional Distribution
| Region | Production Share | Key Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | 55% | Rapid growth, sustainability focus |
| Europe | 20% | Eco-friendly innovations |
| North America | 15% | High demand for low-VOC paints |
| Rest of World | 10% | Emerging markets, infrastructure development |

Frequently Asked Questions about Paint
Not all paints are eco-friendly. Traditional solvent-based paints release high levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that harm the environment. However, water-based paints, low-VOC, and zero-VOC options offer more eco-friendly alternatives. Manufacturers increasingly produce paints with reduced environmental impact, including those made from natural or recycled materials.
Paint can positively impact the environment by enhancing the durability and functionality of buildings and surfaces. For example, certain paints improve thermal insulation or reflect sunlight, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Eco-friendly paints also use sustainable manufacturing processes and materials, minimising waste and pollution.
Yes, paint can contribute to air pollution. The VOCs emitted by many traditional paints react with other pollutants under sunlight to form ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This not only deteriorates air quality but also poses health risks to humans. Choosing low-VOC or zero-VOC paints significantly reduces these emissions.
Some paint pigments can harm the environment, especially those containing heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and chromium. These substances can leach into water sources and soil, posing risks to wildlife and human health. Eco-friendly paints often use natural or non-toxic pigments to mitigate these impacts.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

