Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get up to 4 quotes by filling in only 1 quick form

Install a heat pump for less with the BUS grant

We’ve helped over 500,000 homeowners reduce their carbon footprint
- GreenMatch
- Blog
- Harnessing the Power of Waste Heat with Heat Recovery Systems
Heat Recovery Systems: Comprehensive Guide to Heat Recovery Systems

Heat recovery systems are designed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature while reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainability. These systems transfer thermal energy from one fluid to another or from a solid surface to a liquid at different temperatures and in thermal contact.
The primary purpose of heat recovery systems is to mitigate the energy consumption of buildings for heating, cooling, and ventilation by recovering waste heat.
They can be incorporated into residential or commercial buildings for energy saving and used in various industrial processes. This could include distilleries, food manufacturing plants, and large-scale laundry drying. There are several types of heat recovery systems, including air-to-air heat exchangers, water-to-water heat pumps, geothermal heat pumps, and waste heat recovery systems. Each type has its strengths and suitability for specific circumstances.
For instance, in the United Kingdom, computer data centres have become a significant source of waste heat, an often overlooked byproduct of their high energy usage. As data centres expand due to increasing digital demand, they emit substantial amounts of thermal energy, which typically dissipates into the atmosphere unused.
Recognising this, the focus has now turned towards harnessing this 'wasted' energy using heat recovery systems. Such systems capture and repurpose the excess heat, potentially reducing energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
Heat recovery can significantly improve the overall energy efficiency of data centres, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable operations. This is not only a forward-thinking approach towards energy management but also a critical step towards a more sustainable future for data centre operations.
To understand this further, let's break it down step by step.
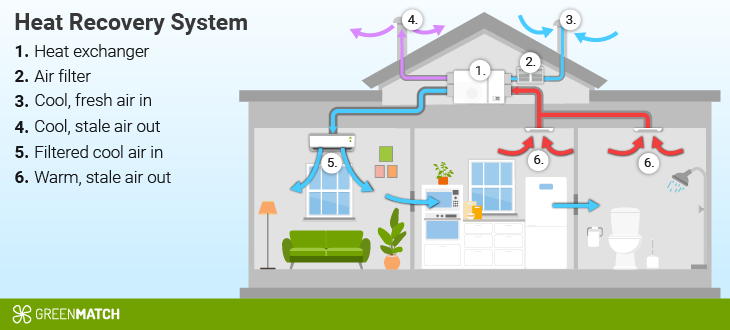
How do heat recovery systems work?
A heat recovery ventilation (HRV) system, or mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (MVHR) system, transfers thermal energy from stale indoor air to fresh incoming air, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature while reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainability.
The system comprises a central heat recovery unit and an air distribution system connected to individual rooms.
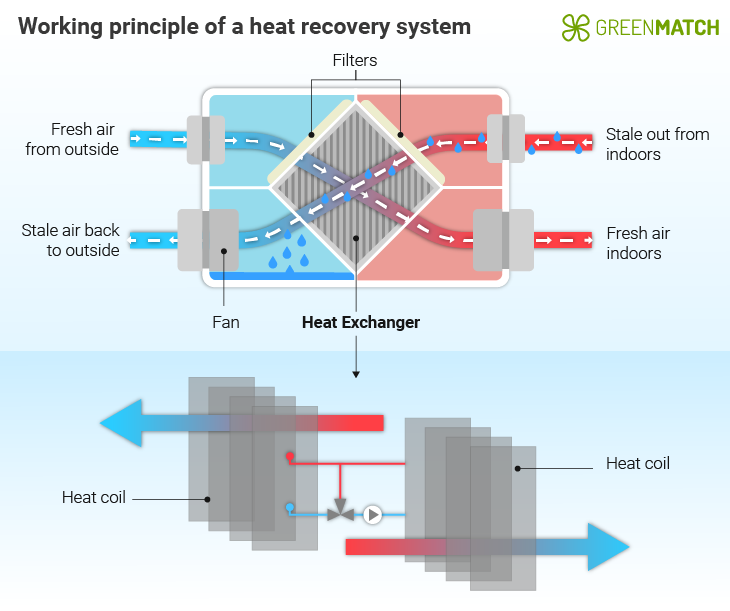
The heat recovery unit moves stale air through pipes while drawing in cold air from the outside via other ducts. The two airflows pass one another within the heat recovery unit, allowing the heat from the stale air to be transferred to the incoming fresh air.
This process is facilitated by a heat exchanger, which acts as a barrier between the two air streams, ensuring indoor air quality is not compromised. The ventilation unit's heat recovery rate determines the system's energy efficiency, with some units capable of recovering up to 85% of the heat in the outgoing airstream.
Types of heat recovery systems
Heat recovery systems, the unsung heroes of energy conservation, hold the key to astonishing benefits that can revolutionise how we utilise energy. These systems maximise efficiency by capturing and reusing waste heat that would otherwise be lost. But did you know that there are different types of heat recovery systems, each with its own set of unique features and advantages?
By understanding the different types of heat recovery systems available, you can decide on the best solution for your specific needs and requirements.
1. Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems (HRVs and ERVs)
HRV systems, also known as Mechanical Ventilation Heat Recovery (MVHR), work by extracting moist, stale air from wet rooms (kitchens, bathrooms, and utility rooms) and supplying fresh, filtered air to habitable rooms (bedrooms, living rooms, and dining rooms). Up to 90% of the heat in the extract air is recovered by the heat exchanger in the unit and used to heat the incoming fresh air. These systems help maintain optimal indoor humidity levels while conserving energy and enhancing comfort. HRVs and ERVs are commonly used in residential and commercial applications, and some local building codes even require installation.
2. Plate heat exchangers
Plate heat exchangers use metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids, providing a larger surface area for heat transfer and increasing the speed of temperature change. They are widely used in various sectors, including domestic heating, hot water systems, and commercial applications. Plate heat exchangers offer low capital investment, installation costs, limited maintenance, and operating costs, making them a cost-effective solution for heat recovery. Plus, they're a great fit for homes where space concerns them.
3. Thermal wheel units
These heat recovery wheels, also known as rotary thermal wheels or thermal wheels, are heat exchangers that use a rotating wheel to transfer heat and moisture between exhaust and outdoor air. This type of HRV is found in large commercial settings where efficiency is paramount. As the wheel rotates, the heat and moisture exchange between the exhaust and outdoor air, providing energy recovery and improved indoor air quality.
4. Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are another heat recovery system that can extract heat from various sources, such as the ground or outdoor air, and transfer it to a building's interior. These systems can help reduce energy costs and improve overall efficiency.
5. Run-Around Coil Systems
Run-around coil systems, also known as closed-loop systems, use a fluid-filled coil to transfer heat between two air streams. These systems suit various applications, including industrial processes and ventilation systems.
6. Integrated Heat Pumps
Integrated heat pumps combine the functions of a heat pump and a heat recovery system, offering a versatile solution for various ventilation and air conditioning applications. These systems capture and reuse thermal energy that would otherwise be wasted, improving energy efficiency, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and increasing total process productivity. This procedure demonstrates the economic and environmental advantages of reusing waste heat.
Benefits of Heat Recovery Systems
Heat recovery systems suit various residential buildings and can be particularly beneficial in areas with harsh climates or poor air quality. By investing in a heat recovery system, homeowners can enjoy improved indoor air quality, reduced energy costs, and a more comfortable living environment. Here are a few benefits of this heat recovery technology.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: These systems help maintain a constant supply of fresh, clean air, reducing indoor air pollution levels and improving the overall air quality in your home. The systems work by extracting stale, moist air from damp rooms in your home and replacing it with fresh, filtered air from outside.
- Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings: Heat recovery systems and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) help reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling by up to 50%, leading to substantial cost savings on utility bills. By reducing the energy consumption for heating and cooling, these systems contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
- Reduction in Humidity and Condensation: Heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) or MVHR systems help control humidity levels and remove excess moisture from the building, preventing mould and condensation issues.
- Healthier Living Environment: Heat recovery systems create a healthier living environment by providing a constant supply of fresh, filtered air. In many commercial cleaners and air fresheners, they help reduce indoor air pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Reduced carbon footprint: These systems contribute to a greener and more eco-friendly future by recovering and reusing wasted heat.
Factors to consider when choosing an MVRH system
Selecting the ideal heat recovery system for your facility is an important decision that requires careful consideration. The MVRH unit is a great option to reduce energy costs and promote sustainability, but selecting the right system that suits your specific needs is crucial. Therefore, several factors must be considered to ensure the best performance and efficiency for your property.
- Energy efficiency: This system can recover 90% of waste heat. It is vital to choose a system designed with energy efficiency in mind and a high coefficient of performance (COP), which measures the amount of energy produced per unit of energy consumed.
- Size and capacity: Not all homes are created equal, and neither are MVHR systems. You must select a system that can meet your facility's heating and cooling needs. Building size, occupancy levels, and the types of processes that the system will power should all be considered. A too-small system will not meet your needs, while a too-large system will be inefficient and costly.
- Maintenance and accessibility: An MVRH system needs regular maintenance to function efficiently. Choose a system designed for easy maintenance and with a low risk of breakdowns. A warranty or service agreement will ensure issues can be resolved quickly and easily.
- Cost considerations: While an MVRH system can save you money over the long term, there will be upfront costs associated with installation. Shop for different models and installation quotes to find the best value for your budget, including maintenance and repair costs.
- Installation and maintenance: The installation process of your MVHR system can be critical. Hiring a professional installer ensures that it's set up correctly for optimal performance. Also, remember that regular maintenance requires cleaning ducts and changing filters.
- Warranty and brand reputation: Pay attention to the warranty and support the manufacturer offers. A robust warranty gives you peace of mind that your investment is protected. Additionally, check for local service providers who can assist with maintenance and repairs.
- Climate considerations and environment impact: Your climate and environment play a significant role in the effectiveness of an MVHR system. In colder climates, the system's heat recovery is more valuable, as it reduces heating costs. In warmer regions, it helps maintain a cool and fresh indoor environment. Choose an MVHR system that aligns with your local climate needs and can considerably reduce your facility's carbon footprint by decreasing energy consumption and waste.
Enjoy year-round comfort: Experience consistent warmth in winter and refreshing coolness in summer. Get the best deal by comparing 3 free quotes.
- Quotes from local engineers
- Payment by finance available
- Save £7,500 with BUS grant
It only takes 30 seconds



Installation of Heat Recovery Systems
The installation of a heat recovery system will depend on the specific needs of your home or workplace. Working with a qualified technician who can assess your needs and recommend the appropriate method for your space is essential.
The installation process for heat recovery systems typically involves the following steps:
- Assessing the building's requirements
- Selecting the appropriate heat recovery unit based on the size and requirements of the building.
- Installing the heat recovery unit in a suitable location, such as the attic or eaves storage.
- Connecting the unit to room air valves via a network of ducting throughout the building.
- Installing external air supply and extraction vents can be wall vents, tile vents, or soffit vents.
- Ensuring proper insulation and sealing of ductwork to prevent heat loss and maintain energy efficiency.
Future Trends in Heat Recovery Technology
Heat recovery systems are a highly efficient and sustainable technology that reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. These systems promote a more sustainable approach to energy utilisation in both industrial and residential settings.
The future of heat recovery systems is expected to be characterised by advanced technologies. Heat pipes, for instance, are being considered for their compact size, low electric energy consumption, and environmentally friendly properties. Additionally, adopting low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants can further enhance the environmental benefits of heat recovery systems. This reduces our reliance on fossil fuels and further reduces carbon emissions.
For instance, the UK government has recently allocated nearly £65 million to support five green heating projects nationwide, including recycling waste heat from large computer systems to supply heating for local communities. The Old Oak and Park Royal Development Corporation in London will be the first to implement this initiative, using £36 million of the funding to construct a heat network that will provide heating to over 10,000 homes and 250,000m2 of commercial space.
Keeping homes warm with waste heat from technology is a glimpse into the future - and demonstrates just how innovative this country can be when it comes to reducing our carbon emissions.
The significance of this topic extends beyond energy efficiency and cost savings. It is also a crucial aspect of sustainability and the future heat recovery systems. As the world continues to grapple with the consequences of climate change, adopting energy-efficient solutions that help reduce carbon emissions is paramount.
As we look ahead to the future of heat recovery technology, one thing is clear: it's a future filled with comfort, sustainability, and innovation. From smart integration to improved air quality and energy efficiency, these trends are shaping a world where our homes are not just places to live but havens of comfort and eco-conscious living.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

