- GreenMatch
- Blog
- 21 Energy Efficiency Myths Debunked
21 Energy Efficiency Myths Debunked
- Many people believe in energy efficiency myths, which can lead to higher bills and increased carbon footprints.
- Leaving appliances on standby wastes power, costing UK households £1.3 billion each year.
- Proper insulation, smart thermostats, and energy-efficient appliances can save homeowners hundreds of pounds annually on energy costs
Energy efficiency myths remain a hot topic of today, potentially hindering our efforts to reduce consumption and combat climate change. These misconceptions not only can cost you money but also increase your carbon footprint, making them a personal and environmental concern.
Recent data from Ofgem, the UK energy regulator, reveals that the average household energy bill is set to rise by 10% from October 2024, reaching £1,717 per year for a typical household. This is significantly higher than the £1,138 average in 2021. The surge makes understanding energy efficiency more crucial than ever.
Despite this increase, a surprising 66% of UK residents still believe in outdated energy efficiency myths, potentially hindering their efforts to reduce consumption and save money. For example, the myth about leaving appliances on standby mode being harmless? It's costing UK households a collective £1.3 billion annually.
Ready to uncover the truth and potentially save hundreds on your energy bills? Let's set the record straight.
The UK's Energy Efficiency Challenge
Climate change has inspired multiple countries to join together to reduce carbon emissions, decrease energy use, and become more sustainable. Many countries have encouraged energy efficiency strategies by offering special tax and financial incentives to homeowners and the elderly.
Currently, 70% of the UK’s household energy is used towards heating. However, this can be brought down by employing some simple Energy-efficacy strategies. But with so many different tips, it’s hard to know which strategies work. Our expert will be clearing popular misconceptions and debunking these popular Energy-Efficiency myths through our unique infographic below:
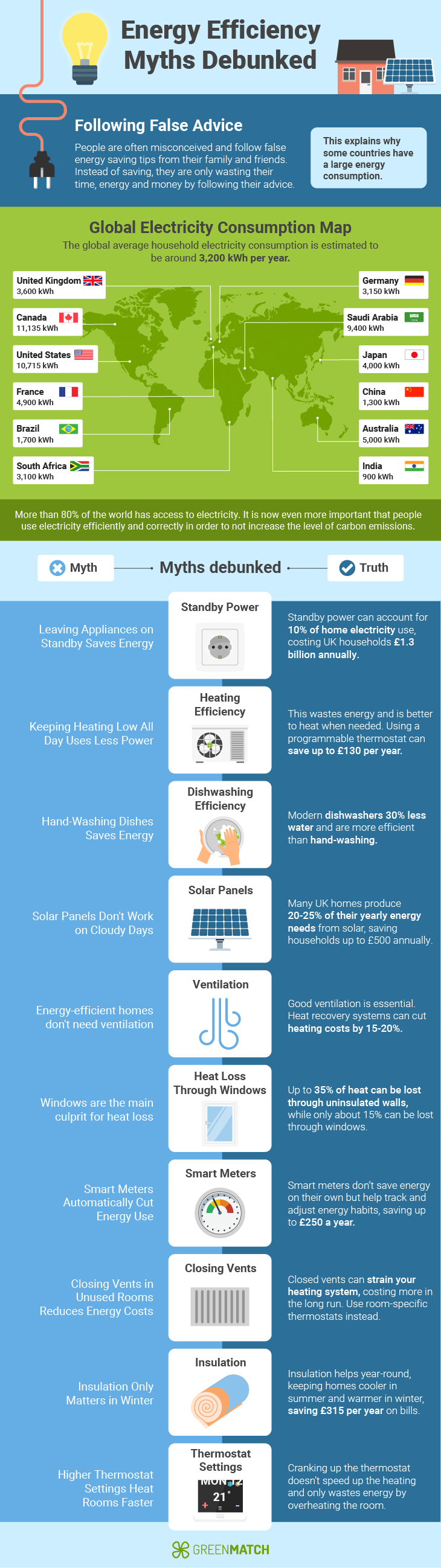
Energy Efficiency Myths Debunked
Energy efficiency is an essential part of reducing carbon emissions and saving on energy bills. Yet, misinformation can lead households and businesses to save money and resources.
Here, we’ll tackle the most persistent misconceptions, explaining the truth behind each and sharing practical, up-to-date strategies to maximise efficiency at home.
Myth 1: Leaving appliances on standby saves energy
Many people believe that devices in standby mode use negligible power. However, this "vampire power" can account for up to 10% of your home's electricity use. The average UK household wastes £55 per year powering devices on standby.
Modern appliances often have advanced features that consume energy even when seemingly off. However, to combat this, using smart power strips or unplugging or turning off devices, ultimately when not in use, can lead to noticeable savings on energy bills.
Myth 2: Leaving the heating on low constantly saves money
Keeping the heating on low all day is more efficient than turning it on and off. In reality, this approach wastes energy and increases bills. Modern heating systems use thermostats or smart home devices to warm homes quickly, making it more cost-effective to heat only when needed. Using a programmable thermostat to control heating times can save up to £130 per year on energy bills.
Studies have shown homes heated on schedules save up to 10% more energy annually than those with constant low-level heating.
Myth 3: Energy-efficient appliances are too expensive
While energy-efficient appliances may have higher upfront costs, they often lead to significant long-term savings. For example, an A+++-rated appliance can save up to £300 over its lifetime compared to a lower-rated model.
For example, upgrading an old refrigerator to an energy-efficient model could save up to 40% on that appliance’s annual energy use, cutting energy bills by £60-£100. Over time, the investment in energy-rated appliances repays itself, especially with ever-rising electricity costs.
Myth 4: Solar panels don't work well in cloudy climates
While solar panels are most effective in direct sunlight, they still generate electricity on cloudy days. Many UK homes produce 20-25% of their yearly energy needs from solar, with payback periods typically lasting about 6-10 years.
As of 2024, the average UK solar panel system can save households £350-£500 annually on electricity bills. Solar panels can gradually gather electricity throughout the year and may be able to power a 3-bedroom family home for a year.
Myth 5: Closing vents in unused rooms saves energy
Contrary to popular belief, closing vents can actually increase energy consumption by forcing the heating system to work harder. Instead, consider using smart thermostats or thermostatic radiator valves to control heating in individual rooms.
Modern systems are designed to distribute air evenly throughout the house. But if you live in one of those old houses, consider installing a modern smart device to help control the energy flow.
Myth 6: Insulation is only for Winter
Energy-efficient homes often provide better comfort levels. Proper insulation, draught-proofing, and efficient cooling and heating systems maintain consistent temperatures throughout all seasons. Well-insulated homes retain heat longer, resulting in greater comfort and lower energy bills.
In warm areas, it helps keep heat out, reducing the load on air conditioning systems. In the UK, improving home insulation can save up to £315 per year on energy bills.
Myth 7: Hand-washing saves more than using a dishwasher
Modern dishwashers are often more efficient than hand-washing, especially when fully loaded. Energy Star-certified dishwashers use about 12% less energy and 30% less water than standard models.
An energy-efficient dishwasher uses about 6-7 litres of water per cycle, while hand-washing typically uses 50 litres and above. For best results, skip pre-rinsing and let the dishwasher do the work.
Myth 8: Thick curtains are as effective as double glazing
While thick curtains can help reduce heat loss, they're not as effective as double glazing. Double-glazed windows can cut heat loss by up to 50% compared to single glazing, potentially saving £110-£140 per year on heating bills.
Over its 20-year lifespan, the savings outweigh installation costs, making it a sound long-term investment.
Myth 9: Smart meters automatically save energy
Smart meters provide real-time energy usage data but don't directly save energy. However, they can help households identify high-consumption periods and adjust habits accordingly. Households who track and adjust their habits can save up to 15% more on energy bills, potentially leading to savings of up to £250 per year.
As of 2024, 31 million smart meters have been installed in UK homes and businesses.
Myth 10: LED bulbs don’t save as much electricity
LED technology has advanced significantly, with prices dropping and efficiency improving. LEDs use up to 90% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and can last up to 25 times longer.
However, if you leave an LED light on unnecessarily, it only adds to your bill. However, switching to LED bulbs can save up to £40 per year on lighting costs.
Myth 11: Insulating older homes is not worth it
While newer homes are often built to higher efficiency standards, older properties can be significantly improved. Effective insulation transforms older homes, often leading to a 20%-30% reduction in heating needs.
Only 15.3% of English and Welsh homes built before 1930 have an EPC rating of 'C' or above, but with proper upgrades, these figures can be dramatically improved. With schemes in place for home insulation grants in the UK, homeowners can access support to make these upgrades affordable.
Myth 12: A bigger boiler means better efficiency
Boilers should be sized based on your home’s heating needs. Oversized boilers can short-cycle, wasting energy and leading to higher bills. Modern boilers and heat pumps, when matched to the home’s size, provide optimal efficiency.
A correctly sized boiler will heat spaces effectively without wasting energy, typically reducing annual costs by about £100. A proper energy assessment by a certified installer helps in selecting the correct size.
Myth 13: Window glazing isn’t cost-effective
While it may be costly upfront, double glazing and triple glazing windows cut heating and cooling losses, reducing annual energy bills by around 50%. These energy-efficient windows significantly reduce heat loss by creating an insulating air barrier.
It is even more efficient with new energy-efficient windows with Low-E glass coatings and advanced sealing that can reduce energy loss by up to 30%, far outperforming older windows that may leak heat.
Annual energy savings from these small measures can range between £150-£300 for an average UK household.
Myth 14: New homes are energy-efficient
While some new homes are generally more energy-efficient than older properties, it's a misconception that all new builds automatically meet the highest energy standards. Recent data shows that 85% of new builds achieve EPC ratings of A or B. However, this means 15% fall below these top ratings, highlighting the importance of checking a property's specific EPC before making assumptions about its efficiency.
Asking for an Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) before buying or renting ensures a new home meets energy efficiency standards, reducing heating and cooling costs.
Myth 15: Electric heating is always cleaner than gas
While electric heating systems can be super efficient, their green credentials are only sometimes clear-cut when they come from renewable energy sources.
For example, if you live in an area where the power grid relies heavily on coal, your electric heater might actually be pumping out more greenhouse gas emissions than a gas boiler.
If you want to electric heating and want to keep your carbon footprint in check, look into renewable energy options. Many energy providers now offer green tariffs that source electricity from wind, solar, or hydropower. By choosing these, you're powering your home with clean energy, making electric heating a much greener choice.
Myth 16: Setting the thermostat higher heats a room faster
This myth is a classic case of wishful thinking. Many of us have been guilty of cranking up the thermostat to 25°C when we are shivering, hoping to warm up our homes in record time. But here's the truth: it will just make your heating system run longer, wasting energy.
Therefore, it is better to set your thermostat to the temperature you actually want. For most UK homes, that's around 18-21°C. Your system will work steadily and efficiently to reach and maintain that temperature. No rush, no waste.
Pro tip: If you are coming home to a cold house, resist the urge to overcompensate. Set the temperature where you want it, and grab a jumper while you wait.
Myth 17: Energy-Efficient Homes Don't Need Ventilation
You might think a super-insulated, airtight home doesn't need fresh air. This doesn't seem right, as even the most energy-efficient houses need good airflow. Good ventilation is essential for indoor air quality and prevents moisture buildup.
Heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems are good examples, as they bring in fresh air while keeping your energy bills in check. These systems can slash your heating costs by 15-20%.
An energy-efficient home is about more than just keeping the heat in. It's about creating a healthy, comfortable living space that's kind to your energy bills, too.
Myth 18: Windows are the main culprit for heat loss
You've probably heard that windows are the biggest heat thieves in your home. Well, that's not quite right. Up to 30 - 35% of heat can be lost through uninsulated walls, while only about 15% is typically lost through windows.
While double-glazing and good curtains are helpful, remember your walls. Proper wall insulation can make a huge difference in keeping your home warm and your energy bills down.
Myth 19: Painting radiators black boosts heat output
You have probably heard the old wives' tale about painting your radiators black to make them more efficient. Well, this is not true at all.
The colour of your radiator doesn't make a lick of difference when it comes to heat output. Whether it's black, white, or hot pink with polka dots, the amount of heat pumped into your room stays the same.
Try adding radiator panels behind them. These cheap and cheerful additions reflect heat into the room instead of letting it escape through the wall. It's like giving your radiator a little energy-saving.
Myth 20: Duct tape is good for sealing ducts
Please stay away from this DIY trap, as it is ineffective for sealing ducts long-term! Duct tape might seem like a quick fix, but it's a poor choice to use to seal anything. The adhesive on duct tape breaks down quickly when exposed to heat and humidity, which is exactly the condition found in duct systems. Within months, that "easy fix" will fail, leaving you right back where you started.
Instead, opt for specialised duct sealants or mastic. These products are designed to withstand the harsh conditions inside the ductwork and provide a lasting seal. For larger gaps or holes, use metal tape or fibreglass mesh before applying sealant.
Proper sealant can boost your system's efficiency by up to 20%. That's a significant saving on your energy bills.
Myth 21: All Insulation Works the Same
Different types of insulation (e.g., cavity, fibreglass, cellulose) suit various climates and home needs. For example, homes without cavity walls or those in high-exposure areas may benefit more from other insulation types.
Loft insulation, for instance, can reduce heating costs by up to 25% annually, while wall insulation provides significant savings in older homes.
Picking the proper insulation is like choosing the right tool for a job. Use the wrong one, and you need to get the best results. Talk to a pro to figure out what's best for your home. It could mean the difference between a cosy, efficient house and one that's burning through energy and cash.
Final Thoughts: Energy-Efficiency Myths
Debunking these energy efficiency myths is crucial for making informed decisions about our energy use. As we have seen, many common beliefs about energy-saving practices that have been debunked today are just the tip of the iceberg.
But they represent common misconceptions that can significantly impact our energy consumption and bills. By embracing accurate information and modern technologies, we can dramatically reduce our energy consumption and costs.
As we move forward, the energy landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and strategies emerging regularly. What works best for one household may not be ideal for another, so it's essential to tailor your approach to your specific circumstances.
By making informed decisions about our energy use, we are not just saving money; we are contributing to a more sustainable future for generations to come.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?