Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get up to 4 quotes from our selected suppliers by filling in only 1 form

Save money by comparing quotes and choosing the most competitive offer

Our service is 100% free and with no obligation
- GreenMatch
- Blog
- Central Heating Systems – The Hydronic System
Central Heating Systems: The Hydronic System
What Is a Central Heating System?
Heating systems represent a combination of equipment that is used to boost the temperature in your household. Various energy sources can be used to power these systems, such as: solar, wood, gas, oil, and electricity. In general, heating systems can be categorised into two basic groups: space heating and central heating.
Central heating systems are known for generating and distributing heat. This is usually done through radiators or underfloor pipes, a boiler, and distribution pipes. These factors as well as your personal requirements, determine the cost of installing central heating. Make sure you consult a trusted boiler installer regarding your heating project beforehand.
Usually, the heat is generated in one location and then evenly distributed throughout the home or building. The boiler doesn’t necessarily have to be situated in a central location, but can be placed anywhere within or adjacent to the structure.
For example, the inhabitants of the Roman Empire were known for using central heating systems, conducting the air heated by furnaces through empty spaces under their floors, a system known as hypocaust. A similar system was used in medieval times in southern Germany, where underfloor channels were used to transfer heat from the furnace room, thus replacing the Roman hypocaust. An example would be the Reichenau Abbey (declared a World Heritage Site in 2000), which used a network of interconnected underfloor channels that heated the 300 m² assembly room during the winter months.
Central heating systems posses a greater heating capacity than a space heater. They transfer the heat using water or air, depending on the distribution system available. Such are: furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps. The most familiar heat source is the combustion of fuel in a furnace or boiler, the resulting heat usually being dispensed/dispersed by air through ductwork, or by water circulated through pipes. Circulating hot water has the advantage of a smaller-sized distribution system (pipes, no ducts), is draft free, which is also known as hydronic heating.
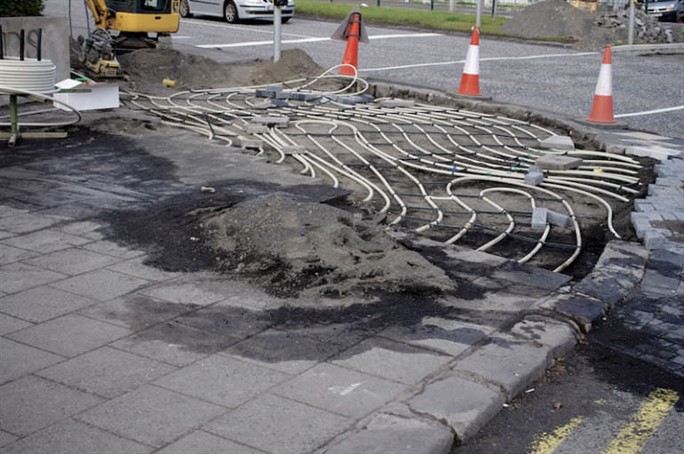
Underfloor Heating in Reykjavik, Iceland

What Is a Hydronic Heating System?
A hydronic heating system (wet system) is dependant on hot water to heat a room or home. The process starts off at the boiler, a pump is sending the water through a pipe distribution system in the house for emanation by using radiators, or the floor itself. As the water cools off, it goes back to the boiler to be re-heated. Due to this system, the objects in your household stay warmer for a longer period of time, thus helping to keep warmth in the house. Alternative heating structures that push fan forced air into your home only warm the air, but not the objects in the room, which will make you spend more money on the running costs. The most recent talks in the industry have stated that heating your home from the floor up rather than vice-versa is much more comfortable and effective.
The hydronic central heating is one of the most efficient and economical alternatives of heating your home. It has become one of the primary choices for house heating in the UK, and also in two thirds of the world. This system is prefered in cooler climates given the fact the energy used to achieve the same level of heat is much lower in a hydronic central system than a ducted heating system, or solely on a heat pump. If you want your hydronic system to perform to its best, it is recommended to equip it with either a geothermal heat pump, or a solar water heater.
Hydronics have started being used extensively in Europe, where the high cost and scarce fuel availability made homeowners to look for the most economical and effective heating options, given how and cost-efficient they can be. A well-designed and installed hydronic system can be very practical in terms of energy use. And if you’re looking for even greater cost reductions, there is the possibility to install a solar thermal system that will allow the sun to heat the water.
The only discomfort with the hydronics is that during the summer, an air-conditioning system needs to be installed if homeowners wish to have a cool temperature during warm weather conditions.
Why Choose a Hydronic Heating System?
Hydronics are usually recommended for new buildings, but that doesn’t mean that you cannot upgrade your own home with such a system. When installing a hydronic heating system into a new building or house, there is considerable initial investment required, but when running at their full potential they can be up to 300% more efficient than electric underfloor heating systems. Hydronics can be combined with radiators or an underfloor pipe system to provide the house with the necessary warmth, although there is the possibility of mixing them both for maximum efficiency. This system is also very safe in comparison to other forms of space heating due to the fact there are no exposed wires or parts.
If you wish to add a hydronic system to your existing household, one of two conditions must be met:
- You’re undergoing refurbishment.
- Reasonable access under the house.
The hydronic heating system has been on the market for some time now, thus the assets have become known to the general public, such as:
- Energy-efficient - water has proven to be 4 times more efficient than electricity at transporting heat.
- Comfortable - The heat is distributed evenly, starting at the feet and it doesn’t give the room a stuffy ambiance.
- Concrete slab continues to emanate warmth even after you turn heating off.
- Benefit from room-by-room controls.
- Low-maintenance - no ducts or grilles that need dusting.
- A hot water heat pump recommended for even greater energy savings.
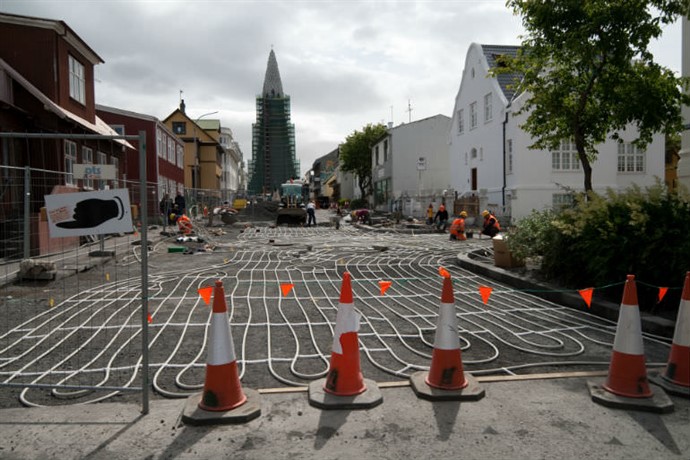
Underfloor Heating in Reykjavik, Iceland

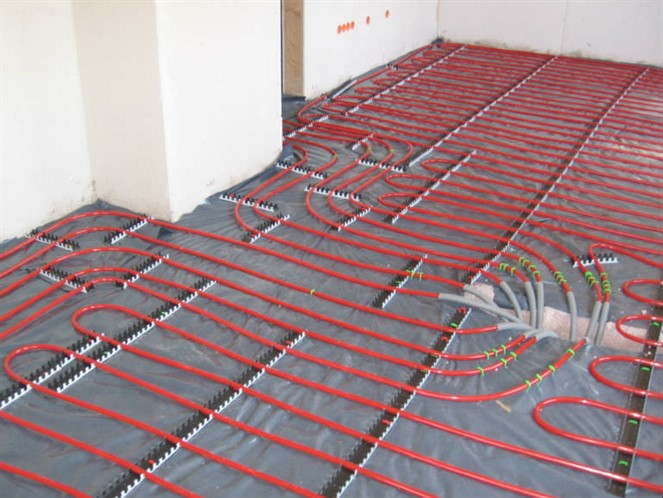
Hydronic Heating System - Are They Worth the Investment?
Experience in this field has shown that even identical households can experience drastically different rates of heat loss based on the types of heating systems built in. Buildings with hydronics have frequently displayed lower energy usage than structures with forced-air heating systems. There a few key differences between the air to air heating and hydronics, which are:
- The hydronic heating system offers a more efficient and economical performance, 1 kg of air brings a quarter of the heat and occupies over 800 times the volume of 1 kg of water.
- Hydronics provide an even, less oscillating temperature than the forced-air system.
- It won’t dry out the inside air as much.
- You will prevent any dust, pollen, mould, and allergens being introduced into your house.
Recent studies that have compared several hundred homes, some with forced-air systems, others with a hydronic heating system, discovered air leakages at an average 26% higher, and energy usage at 40% greater in households using air heating.
Another factor that affects your home energy use is the air temperature stratification. There is a tendency of warm air to rise to the ceiling, while cool air goes straight to the floor. In intense conditions the difference in air temperature between floor and ceiling can even exceed 20 degrees Celsius.
Stratification has the tendency to get worse when it involves high ceilings, poor air circulation, heating systems that supply air in rooms with high temperatures. Maintaining a decent air temperature in rooms with a high degree of temperature stratification usually leads to higher air temperatures near the ceiling, hence the hot air increases the chances of losing heat through the ceiling.

Advantages of Installing a Hydronic Heating System
As mentioned above, although the initial installation costs are relatively high, there are numerous long-term advantages such as:
- It can be installed into almost any existing building, on various levels.
- After installation, it will save you money on running costs.
- The system is environmentally sustainable.
- Hydronics are very flexible, it can be installed in stages. You are able to add more heating areas, therefore for every extension, or renovation you simply plumb in the new components.
- It’s very efficient, water representing a low cost effective heat exchange agent.
- You can take individual control of every radiator or floor zone in the house, easy to fix the temperature in any room.
- The hydronic system in combination with heat pumps is designed to pass the test of time. Maintained properly, the system can surpass any other form of heating.
In conclusion, more and more viable environmentally-friendly technologies have emerged on the market in order to reduce the carbon footprint, and the hydronic heating system is definitely in this category. If you’re thinking about installing such a system, we at GreenMatch are here to help you get the best deal there is. Our services offer quotes for all the sustainable technologies approved by the UK government.
Fill in the form in just 1 minute
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?