Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Get up to 4 quotes from our selected suppliers by filling in only 1 form

Save money by comparing quotes and choosing the most competitive offer

Our service is 100% free and with no obligation
- GreenMatch
- Blog
- 10 Countries Producing Most Plastic Waste
Top 10 Countries Producing Most Plastic Waste

The growing problem of plastic waste pollution severely impacts our environment. Plastic waste is produced yearly in landfills, oceans, and natural areas. To remedy this problem, global action is urgently required. Over the years, 9.2 million and 12.7 million tonnes of plastic have been generated, with one trash truck's worth of plastic waste in the ocean every minute. If they do biodegrade, it may take hundreds of years.
According to UN Environment Programme research (UNEP), if current trends continue by 2050, fewer fish will be due to plastic waste. On an annual level, plastic waste generated per person averages 221 kg in the United States and 114 kg in European OECD countries to 69 kilogrammes on average.
The highest total plastic waste per capita
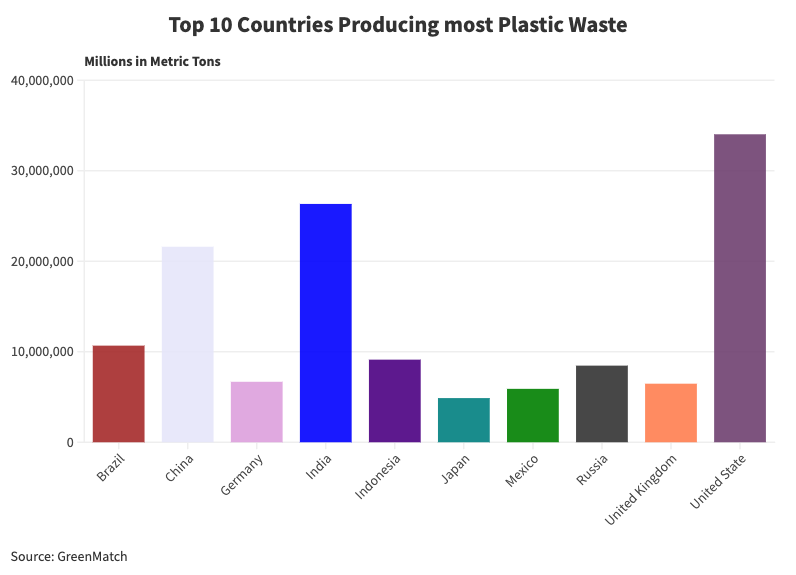
Despite our efforts to minimise plastic consumption, ten countries stand out for generating the most plastic waste globally. Some countries have a considerable responsibility to combat the ongoing plastic waste crisis that threatens the health of our planet.
Plastic use has increased significantly in the United States over the previous four decades, with at least 85% of municipal plastic waste disposed of in landfills. The United States produces over 42 million metric tonnes of plastic waste each year, which equates to approximately 130kg of rubbish for every American. The recycling rate for plastic waste in the United States is declining, with only 5-6% recycled as of 2021 statistics. The infrastructure has failed to keep pace with the massive growth in American plastic production. This results in mismanagement, incinerated, and inefficient waste disposal in landfills, causing up to 2.2 million tonnes of plastic to "leak" into the environment.
India is one of the world's most significant contributors to plastic waste, generating about 9.46 million tonnes annually. The country is currently facing a severe challenge with plastic waste. The amount of plastic waste generated in the country is staggering and is becoming a growing environmental concern. The root cause of this issue is the need for proper waste management infrastructure in India, which leads to littered streets, overflowing landfills, and plastic waste infiltrating water bodies.
With the negative effect of massive tonnes of plastic waste annually, of which 40% goes uncollected, the Indian government is fighting back by introducing an initiative, the Plastic Waste Management Rules. These programs aim to reduce the use of single-use plastic, increase recycling, and promote proper waste management while raising awareness about the issue.
China is the biggest producer of plastic, with about 60 million tonnes of plastic waste, yet only 16 million tonnes were recycled. However, the country has taken steps to combat plastic waste pollution, including a ban on single-use plastics and a focus on the circular economy. The regulatory focus and fiscal investment in solid waste management and infrastructure. With as much as 70.6% incinerated, recycled, and mismanaged, triggering environmental problems, per capita plastic consumption is well behind the United States.
The plastic waste problem in Brazil is a pressing issue that demands urgent attention. The world's fourth largest producer of plastic waste, behind only the USA, China, and India, produces about 11.3 million tons annually, of which only 1.28% is recycled. This means that a significant amount of plastic waste ends up in landfills, mismanaged or in the ocean, posing a severe threat to the environment and marine life. Of Brazil's single-use plastic items each year, 13% are products such as plates, glasses, cutlery, plastic bags, and straws, contributing to Brazil's plastic waste problem.
It is concerning that Japan, a country known for its environmental awareness and cleanliness, is facing a severe plastic waste problem. Japan produces around 9 million tons of plastic waste annually, with more than 40% of disposable plastic, such as packaging and food containers. Despite being one of the largest consumers of plastic packaging globally, much of this waste ends up in landfills or the ocean, posing a significant threat to the ecosystems. The recycling rate of waste in Japan is 19.9%. Although the country has an efficient method of collecting recyclable materials, a significant amount of plastic waste is either incinerated or exported to other countries for processing.
Indonesia generates approximately 7.8 million tons of plastic waste annually, with 4.9 million tons being mismanaged, such as uncollected waste, disposed of in open dumpsites, or leaked from improperly managed landfills. Plastic waste has affected Indonesian rivers and the ocean, with more than 600,000 tonnes of plastic dumped, mostly from rural areas, due to an uncollected system. This has led to the Indonesian government launching a program that will pay thousands of traditional fishers to collect plastic trash from the sea, aiming to reduce marine plastic waste by 70% by 2025.
Russia's plastic waste production is increasing, and it is one of the few countries whose plastic waste output is increasing to 8.47 million tons. The country faces significant challenges with inadequate waste management systems, a lack of recycling infrastructure, and insufficient awareness. Although some recycling programs are in place, they are not widely available or well-established.
Germany is one of Europe's biggest producers of packaging waste, especially plastics, despite being celebrated as a world leader in recycling. The country generates approximately 6.5 million tons of plastic waste pollution each year, with a considerable portion originating from packaging materials. According to Philipp Sommer, a circular economy expert, Germany recycles much less plastic packaging waste than commonly understood, with only 38% recycled plastic waste.
The United Kingdom is one of the world's most significant sources of plastic waste per person contributing to approximately 6.4 million tonnes of plastic waste. Despite the government's best efforts, the country still generates considerable plastic waste, and the recycling infrastructure must keep pace with the significant growth. To address these challenges, the UK government has implemented several measures to reduce plastic waste, such as the plastic bag charge and the ban on microbeads, which ends up in landfills.
Mexico is one of the countries that suffer from plastic pollution, with 5.9 million tons of plastic waste being a significant contributor to environmental degradation, with only 15% being recycled. Although Mexico has a high % percentage collection rate of 91%, most of this waste is improperly disposed of in unregulated landfills or enters the environment as litter. This improper disposal leads to incineration, which releases toxic chemicals into the air. The issue is particularly severe in Mexico City, the country's capital, which generates an estimated 13,000 tons of waste per day, up to 40% of which is plastic.
Although these nations generate substantial volumes of plastic waste statistics with minimal recycling, some are better at processing plastic waste safely. In contrast, middle-income and low-income countries still developing their infrastructure tend to produce more mismanaged waste plastic. The severity of the plastic pollution predicament plaguing portions of Asia, specifically India, China, and Indonesia, where mismanaged plastic refuse has reached critical levels, cannot be overstated.
The diverse methods by which countries deal with discarded plastics largely depend on a nation's economic status. This is because wealthier countries are generally able to either incinerate, recycle, or adequately landfill their plastic refuse. However, less affluent societies have no choice but to dispose of such detritus through uncontrolled dumping or open burning.
Although low-to-middle-income countries sadly struggle with mismanaged plastic waste pollution that ultimately flows into their waterways, seas and ocean. Though intertwined and multi-faceted, the proliferating problem of plastic pollution demands collaborative and coordinated worldwide countermeasures.
Environmental Impact of Plastic Waste
The adverse effects of plastic waste on the climate are numerous and far-reaching. Once hailed as a "phenomenon material," plastic has become one of the most burning environmental issues encyclopedically. This is our reality today, as plastic waste significantly wreaks havoc on our biodiversity, ecosystems, animal and plant life, and human health.
As plastic waste pollution requires immediate attention, we start by using reusable material rather than a disposable commodity that's quickly discarded. It is alarming to note that the global recycling rate for plastic waste is a mere 9%, while a staggering 22% needs to be adequately managed. This means using fewer materials to make plastic more easily recyclable or biodegradable. Increasing recycling facility availability will limit the number of polymers in manufacturing.

Carbon footprint reduction
Several countries have enforced successful actions and programs to reduce plastic waste products and enhance disposal methods. Germany has joined a transnational coalition to tackle plastic waste. The " Plastic Free July" program encourages individuals and businesses to reduce plastic consumption and waste in Australia.
Meanwhile, Norway has introduced a plastic bottle deposit system, resulting in a high recycling rate and reduced plastic waste. Plastic waste pollution is predicted to increase from 9% in 2019 to 17% in 2060, with more incineration and landfilling. Nevertheless, plastic waste is projected to increase utmost in non-OECD countries, driven by profitable growth in rising economies in Africa and Asia.

Reducing plastic waste
To protect the environment, vigorous measures must be taken to limit plastic trash production and enhance disposal procedures. One efficient strategy to accomplish this is to promote reusable bags and containers, which have been shown to reduce the quantity of plastic trash generated drastically. Investing in improving recycling infrastructure and technology is also critical to ensuring that more plastic waste is recycled rather than ending up in landfills or the oceans.
Collaboration between governments and businesses can aid in developing policies and incentives that encourage using sustainable materials and practices. Adopting a holistic approach to reducing plastic waste will pave the road for our world's cleaner and healthier future.
Re-Looping as a Solution
The United States generates more than ten times the daily per capita plastic waste of countries like India. Plastic buried deep in landfills can leach harmful chemicals that spread into groundwater. The procurement and polymerisation of petrochemicals to produce plastics fuel the continual combustion of nonrenewable fossil fuels. This has led consequent emanation of greenhouse gases, intensifying the precarious perturbations in global temperatures and weather patterns.
Therefore, individuals can take action by reducing plastic use and participating in waste collection. Supporting policies on reduced plastic packaging is a significant step toward reducing the statistics on plastic waste. Let's work together to safeguard our environment and create a sustainable future for future generations.

Inemesit is a seasoned content writer with 9 years of experience in B2B and B2C. Her expertise in sustainability and green technologies guides readers towards eco-friendly choices, significantly contributing to the field of renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
We strive to connect our customers with the right product and supplier. Would you like to be part of GreenMatch?

